- Volume 60 , Number 4
- Page: 676–709
Current literature
This department carries selected abstracts of articles published in current medical journals dealing with leprosy and other mycobacterial diseases.
CHEMOTHERAPY
Fleming, C. M., Branch, R. A., Wilkinson, G. R. and Guengerich, F. P. Human liver microsomal N-hydroxylation of dapsone by cytochrome-P-4503A4. Mol. Pharmacol. 41(1992)975-980.
One of the major routes of elimination of dapsone (4,4'-diaminodiphenylsulfone) is by N-oxidation, to produce a hydroxylamine metabolite. The specific form of cytochrome P-450 (P-450) involved in this oxidation reaction was examined in human liver microsomal preparations previously characterized with respect to their content of several known P-450 enzymes. Among five preparations, the rank order of activity for dapsone hydroxylaminc formation was most well correlated with the immunochemically determined level of P-4503A4 (r = 0.94, p < 0.03). Moreover, inhibition of microsomal oxidation was observed with antibodies specific to P-4503A, with a maximum reduction of > 90%, but was not produced by antibodies specific to P-4501A2, P-4502C(MP), or P-4502E1. Prior incubation of microsomes with gestodene (100 µm) or troleandomycin (20- µm), known selective mechanism-based inhibitors of P-4503A enzymes (in the presence of NADPH), led to 75% and 40% reductions in catalytic activity, respectively. In contrast, preincubation with increasing concentrations of alpha-naphthoflavone, a known activator of P-4503A4, increased dapsone N-hydroxylation in a concentration-dependent manner, with fivefold activation being observed at 50-µm alpha-naphthoflavone. Finally, P-4503A4 isolated from human liver microsomes and cDNA-expressed P-4503A4 (in yeast) were both able to catalyze dapsone N-hydroxylation, with the latter preparation exhibiting a threefold activation in the presence of 100-µm alphanaphthoflavone. Collectively, these findings demonstrate that N-oxidation of dapsone in human liver is predominantly mediated by P-4503A4, and they suggest that quantitative measurement of this metabolic pathway in vivo might serve as an index of the activity of this enzyme. -Authors' Abstract
Hu, L.-F., et al. [An observation of multibacillary cases of leprosy the second year after stopping MDT in Xichang City, Sichuan Province.] China Lepr. J. 7(1992)202-204. (in Chinese)
Seventy cases of multibacillary (MB) leprosy have been monitored over 2 years after completing a course of WHO's MDT in Xichang city, of Sichuan province, included 13 originally new cases whose skin lesions had subsided 1 year after stopping MDT and of which 12 cases have become negative in BI in the second year of monitoring. After cessation of MDT, 1 of the 13 cases incurred ENL and 5 cases had type 1 reaction (38%). Among the 70 monitored cases, 57 had taken DDS and other antileprosy drugs, most of their skin lesions subsided and their BI was lower before MDT, of which 56 (98.24%) have been negative bacteriologically in the second year of the monitoring. No relapse was found.-Authors' English Abstract
May, D. G., Arns, P. A., Richards, W. O., Porter, J., Ryder, D., Fleming, C. M., Wilkinson, G. R. and Branch, R. A. The disposition of dapsone in cirrhosis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 51(1992)689-700.
Acetylation and N-hydroxylation of dapsone were evaluated in drug-free, nonsmoking, normal subjects and subjects with cirrhosis (N = 7 for each group) after oral administration of 100 mg dapsone. Acetylation was not correlated with oral dapsone clearance or reduced in cirrhosis (0.37 ± 0.43 vs 0.52 ± 0.32). Fractional metabolic clearance of dapsone to its hydroxylaminc was associated with dapsone oral clearance (r = 0.96, p < 0.001, N = 14). In patients with cirrhosis, liver disease was associated with a trend to reduction in oral clearance (22%) and metabolic clearance of dapsone (48%). Protein binding was minimally reduced by cirrhosis (73% ± 1% vs 69% ± 3%) in patients with cirrhosis (p < 0.02). The dapsone recovery ratio was validated as a phenotypic index of the metabolic clearance of dapsone (r = 0.74, p < 0.05). In an extended comparison of 14 patients with cirrhosis to 70 control subjects, cirrhosis was associated with reductions of 28% in dapsone recovery ratio (p < 0.001), and 37% in acctylation ratio (p < 0.01). Neither dapsone recovery ratio nor acctylation ratio correlated with Pugh Score, conventional liver function tests, indocyanine green clearance, or phenotypic measures of S-mephenytoin hydroxylase or debrisoquin hydroxylase activity. We conclude that cirrhosis is associated with minor changes in dapsone disposition and that dosage modification is not required. In addition, there is evidence that cirrhosis has a selective influence on activity of individual isozymes of cytochrome P450.-Authors' Abstract
Outman, W. R., Levitz, R. E., Hill, D. A. and Nightingale, C. H. Intraocular penetration of rifampin in humans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36( 1992)1575-1576.
The penetration of rifampin into human aqueous humor was determined in 15 patients undergoing elective cataract surgery. Between 0.9 hr and 5.5 hr after administration of a single 600-mg oral dose, concentrations ranged from 6.0 to 21.5 mg/liter in serum and from < 0.2 to 1.3 mg/liter in aqueous humor.-Authors' Abstract
Perez Gallardo, L., Blanco, M. L., Soria, H. and Escanero, J. F. Displacement of rifampicin bound to scrum proteins by addition of levamisole. Biomed. Pharmacother. 46(1992)173-174.
We have studied, by ultrafiltration, the interactions between rifampin (15 and 30 µm) and levamisole (7 µm) since both drugs may be associated for the treatment of brucellosis. We can observe a statistically significant increase in the free plasma fraction of rifampin at the studied concentration of levamisole, which indicated that levamisole reduced rifampin bound to proteins (290% and 250%, respectively). -Authors' Abstract
CLINICAL SCIENCES
Chaturvedi, R. M. and Kartikeyan, S. Suggested new technique for skin biopsy under field conditions. (Letter) Lepr. Rev. 62(1991)432-433.
The correspondents describe a technique (illustrated by a line drawing) used by them for assessing the immunotherapeutic efficacy of the ICRC vaccine against leprosy in India. In brief, a fine-bore needle is used to infiltrate the selected skin site with local anesthetic. The same needle is then inserted subcutaneously through the skin so that a piece of skin can be lifted up. An elliptical cut (about 10 mm in length) is made with a scalpel around the needle, and the tissue is transferred to a vial containing fixative. A single suture made of absorbable material is used to close the incision, and the site is dressed to prevent secondary infection. The technique is stated to be quick, simple, and suitable for routine use under field conditions.-C. A. Brown (Trop. Dis. Bull.)
Kyriazopoulou, V. and Vagenakis, A. G. Abnormal overnight dexamethasone suppression test in subjects receiving rifampin therapy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 75(1992)315-317.
We have studied the effects of rifampin on the overnight 1-mg dexamethasone suppression test usually employed to exclude suspected Cushing's syndrome. Previous observations indicate that in humans, rifampin profoundly attenuates the biological effects of hydrocortisol and prednisolone, probably by increasing the metabolism of these drugs in the liver. The study was carried out in 16 normal volunteers. All subjects had a normal overnight 1-mg dexamethasone suppression test (468 ± 86 vs 32 ± 21 nmol/L; mean ± SD). In 8 subjects treated with rifampin (600 mg) for 10 days, the inhibitory effect of dexamethasone on serum Cortisol was completely prevented (575 ± 114 vs 434 ± 82). In the remaining 8 rifampin-treated subjects, the inhibitory effect of 1, 2, or 3 mg dexamethasone on serum Cortisol was not observed. When 4 mg dexamethasone were administered, the scrum Cortisol level was 193 nmol/L, above the expected normal suppression value. The plasma dexamethasone concentration was very low after rifampin treatment (range, 1.2-4.8 nmol/L). We conclude that when patients are treated with rifampin, the standard overnight dexamethasone suppression test not only had no diagnostic value, but can be very misleading.-Authors' Abstract
Lu, T.-C, et al. [Analysis of roentgenograms of bones and joints in leprosy.] China Lepr. J. 8(1992)21-23. (in Chinese)
Roentgenograms of the bones and joints of feet and ankles have been collected from 54 leprosy patients and analyzed. The results showed that there are specific changes in 14 cases (25.9%), most of which are cystoid changes and located in the epiphyseal end of metatarsal bones and palanges, but bone expansion is minimal. Forty-eight cases (88.9%) had nonspecific changes in the metatarsal and phalangeal bones and only a few of the cases showed changes of tarsal bones and ankle joints. Secondary infections in them mainly included chronic osteomyelitis and periostitis. Joint destruction presented as complete and incomplete dislocations, of which severe ones are like Charcot's arthropathy and some of them showed obscurity of articular surface, stenosis of joint space and ankylosis or joint fusion. The authors suggest that regular roentgenographic examination of bones and joints should be done for hands, feet, wrists and ankles of leprosy patients so as to find out pathologic changes in them in time for preventing deformity. -Authors' English Abstract
McGeer, P. L., Harada, N., Kimura, H., McGeer, E. G. and Schulzer, M. Prevalence of dementia amongst elderly Japanese with leprosy-apparent effect of chronic drug therapy. Dementia 3(1992)146-149.
The overall prevalence of dementia in 1410 Japanese leprosy patients 65 years or over continuously treated with dapsone or closely related drugs was 2.9%. This compares with 4.83% of 621 cases treated intermittently and 6.25% of 1761 cases untreated for at least 5 years. Multiple logistic regression analysis showed a highly significant increase of dementia with age (p = 0.0001) and, after age adjustment, a significant reduction of dementia in drug-treated compared with drug-free patients (p = 0.017). Such treatment had no significant effect on the prevalence of strokes. These data suggest that dapsone and closely related drugs may have potential use as agents. - Authors' Abstract
Weiss, M. G., Doongaji, D. R., Siddhartha, S., Wypij, D., Pathare, S., Bhatawdekar, M., Bhave, A., Sheth, A. and Fernandes, R. The explanatory model interview catalogue (EMIC) -contribution to crosscultural research methods from a study of leprosy and mental health. Br. J. Psychiatry 160(1992)819-830.
The Explanatory Model Interview Catalogue (EMIC) has been developed to elicit illness-related perceptions, beliefs, and practices in a cultural study of leprosy and mental health in Bombay, India. Leprosy is an especially appropriate disorder for studying the inter-relationship of culture, mental health and medical illness because of deeply rooted cultural meanings, the emotional burden, and underuse of effective therapy. Fifty percent of 56 recently diagnosed leprosy outpatients, 37% of 19 controls with another stigmatized dermatological condition (vitiligo), but only 8% of 12 controls with a comparable nonstigmatized condition (tinea versicolor) met DSM-III-R criteria for an axis I depressive, anxiety or somatoform disorder. Belief in a humoral (traditional) cause of illness predicted better attendance at clinic-Authors' Abstract
Weng, S.-M., et al. [GPAT with dried blood specimens for detection of antibody to PGI of M. leprae.] China Lepr. J. 7(1991)215-218. (in Chinese)
A comparison of gelatin particle agglutination tests (GPATs) by the use of sera and dried blood on filter paper was made in 197 cases of leprosy who had been cured with only DDS. The results showed that the coincidence rate between the two is 88%, and the positive rate is 27.9% in the former and 36.5% in the latter. The coincidence rate of the titers in the two methods is 80%, but the differences between the both with one titer is 13% and with two titers is 6%. The controlling survey between GPAT and PGL-ELISA in 599 cases of leprosy cured only with DDS showed that the specificity and sensitivity of GPAT are 94.3% and 93.9%, respectively. Among the cures with positive GPAT the relapse rate was 9.6% in original MB, and 4.5% in original PB, but among those with negative GPAT no relapse was found. The dried blood is made from 20 µg of earlobe blood, amounting to 8 µg of the serum, but because of the pressure of the sampling it might contain a few tissue fluids, and therefore it is better to add only 108 µg of the diluent to it. -Authors' English Abstract
IMMUNO-PATHOLOGY
Adeleye, T. A., Colston, M. J., Butler, R. and Jenner, P. J. The antibody repertoire to proteins of Mycobacterium leprae: genetic influences at the antigen and epitope level. J. Immunol. 147(1991)1947-1953.
The effects of both H-2 and non-H-2 genes on the antibody response to the proteins of Mycobacterium leprae were investigated. Using a BIO series of congenic mice [the authors] found that the repertoire of antibody responses was under H-2 gene control, and that non-H-2 genes were also involved. By Western blotting, differences in the number and m.w. of proteins recognized by mice of different genetic background were apparent. Such differences were also reflected in the total antibody response to a soluble extract of M. leprae (M. leprae sonicate), as measured by ELISA. Concentrating on one particular antigen, the 65-kDa heat shock protein, [they] found that all strains of mice developed antibodies following immunization with the purified recombinant protein, although there was a continuous distribution in the titer of antibodies obtained, with differences between individual strains indicating both H-2 and non-H-2 effects. Using a library of overlapping peptides based on the amino acid sequence of this protein, [the authors] have mapped the B-cell epitopes in the different strains of mice. H-2 genes had no effect on the structure and number of epitopes recognized, although this was influenced by non-H-2 genes. There was a high level of concordance between actual epitopes recognized and those predicted by calculations of antigenic index, and B-cell epitopes were located in similar positions to previously determined T-cell epitopes.- Authors' Abstract
Appelberg, R. Interferon-gamma (IFNgamma) and macrophage inflammatory proteins (MIP)-l and (MIP)-2 are involved in the regulation of the T-cell-dependent chronic peritoneal neutrophilia of mice infected with mycobacteria. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 89(1992)269-273.
In mycobacterial infections of mice there is a chronic, immune-mediated mobilization of neutrophils to the infectious site. In this study we evaluated the role played by cytokines in the chronic peritoneal neutrophilia which occurs in mice intraperitoneally infected with Mycobacterium bovis BCG or M. avium. Antibodies to IFN-gamma and to MIP-1 and MIP-2 were effective in reducing peritoneal neutrophilia when given during the infection. Whereas the former antibody was only effective when given early, the latter two were effective when administered late in infection, suggesting the MIPs were direct mediators of neutrophil recruitment. Recombinant IFN-gamma given intraperitoneally induced the accumulation of neutrophils and primed the peritoneal cells for an enhanced recruitment of neutrophils. Our data show that chronic neutrophilia during mycobacterial infection is regulated by different cytokines acting at different stages and levels of neutrophil recruitment.-Author's Abstract
Barnes, P. F., Chatterjee, D., Abrams, J. S., Lu, S. H., Wang, E., Yamamura, M., Brennan, P. J. and Modlin, R. L. Cytokine production induced by Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan - relationship to chemical structure. J. Immunol. 149(1992)541-547.
Lipoarabinomannan (LAM), a major cellwall component of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, exhibits a wide spectrum of immunoregulatory efTects. To identify cytokines produced by human PBMC in response to LAM, we used PCR amplification to detect cytokine mRNA. LAM-induced transcription of mRNA for cytokines characteristically produced by macrophages, including TNF, granulocyte-macrophage-CSF, IL-1-alpha, IL-l-beta, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10. In contrast, LAM did not induce transcription of mRNA for cytokines produced predominantly by lymphocytes, such as lymphotoxin, IFN-gamma, IL-2, IL-3, or IL-4. Measurement of concentrations of TNF, granulocyte-macrophage-CSF, IL-6, IL-10, IFN-gamma, IL-2, and IL-4 in cellculture supernatants indicated that cytokine release correlated with mRNA patterns. Lipomannan (LM) and phosphatidylinositol mannosides (PIM) are simpler versions of LAM. LM lacks arabinan; whereas PIM lacks both arabinan and most mannan residues. LAM, LM, and PIM induced transcription of cytokine mRNA, elicited cytokine production, and suppressed Ag-induced T-cell proliferation, indicating that most of the biologic activity of LAM was associated with the phosphatidylinositol end of the molecule. In support of this conclusion, deacylation of LAM abrogated its capacity to induce cytokine production and suppress Ag-induced proliferation. The production of macrophage-derived cytokines induced by LAM may mediate clinical manifestations of tuberculosis, such as fever, weight loss, and tissue necrosis, as well as immunoregulatory efTects such as inhibition of Ag-induced proliferation and hyperglobulincmia. -Authors' Abstract
Blanchard, D. K., McMillen, S., Hoffman, S. L. and Djeu, J. Y. Mycobacterial induction of activated killer cells-possible role of tyrosine kinase activity in interleukin-2 receptor alpha expression. Infect. Immun. 60(1992)2843-2849.
Mycobacterium avium is an intracellular opportunistic pathogen commonly seen in AIDS patients. M. avium-infected monocytes have been recently shown to be lysed by interleukin-2 (IL-2)-activated killer cells. Since some bacterial products can directly augment natural killer activity, we examined the ability of these microorganisms to induce killer-cell activity. Coculture of M. avium with large granular lymphocytes (LGL) was found to augment the ability of LGL to lyse both tumor cells and bacterially infected autologous monocytes. The induction of tumoricidal activity by M. avium was only partially neutralized by the presence of anti-IL-2 antibodies, indicating that both IL-2-dependent and IL-2-independent mechanisms are responsible for activation of killer cells. Furthermore, only the direct interaction between bacterium and LGL could induce the expression of both IL-2 receptor alpha protein and mRNA, an effect which was abrogated by the presence of genistein, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Thus, M. avium was seen to induce killer cells, an activity that is concomitant with the upregulation of IL-2 receptor alpha, or Tac antigen, expression and which involves signal transduction mechanisms mediated by tyrosine kinase activity. -Authors' Abstract
Campbell, G. and Cree, I.A. Macrophage and epithelioid cell nuclear morphology in leprosy. Pathol. Res. Pract. 188(1992)625-629.
The spectrum of disease in leprosy is characterized by the presence of macrophages in lepromatous lesions and epithelioid cells in tuberculoid granulomas. Since changes in nuclear shape occur during macrophage activation, we have measured nuclear morphology by planimetry in biopsies across the leprosy spectrum. The results show no significant correlation of any of the parameters of nuclear morphology measured between different lesions or between biopsies from the center and edge of the same lesion. There were no différences between the Ridley-Jopling groups. However, several parameters which measure the degree of ellipticity of the nuclei showed strong correlation with granuloma size in untreated leprosy patients. This suggests that local pressure effects may influence epithelioid cell and macrophage nuclear morphology in leprosy lesions. -Authors' Abstract
Damasco, M. H. S., Sarno, E. N., Lobao, A. S., Alvarenga, F. B. F., Porto, J. A., Rosankaimer, F. and Kaplan, G. Effect of cutaneous cell-mediated immune response to rIFN gamma on Mycobacterium leprae viability in the lesions of lepromatous leprosy. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 25(1992)457-465.
Studies were carried out to determine the effect of intradermal injections of recombinant human interferon-gamma (rlFNgamma) on the viability of Mycobacterium leprae. Twenty-three untreated and 4 treated multibacillary patients, 12 with lepromatous leprosy (LL) and 15 with borderline lepromatous leprosy (BL), were selected for intradermal administration of rlFN-gamma or PPD. Treated patients (LL and BL) had received multidrug therapy according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization, i.e., rifampin (600 mg/ month), dapsone (100 mg/day) and clofazimine (50 mg/day and 300 mg/month) for 1-4 months. Three daily doses of 10 or 30 µg rIFN-gamma induced local induration and mononuclear leukocyte accumulation. Bacteria isolated from a punch biopsy of the site 21 days after lymphokine administration were injected into mouse foot pads and evaluated for viability and growth. The local response to rIFN-gamma (specific activity 2 × 107 units mg protein) induced a delay or total inhibition of M. leprae growth in the mouse foot pad, indicating that the cellular response to the antigen reduced local M. leprae viability. The extent of reduction in viability depended on the dose of rIFN-gamma injected and the extent of local induration induced by the lymphokine. With a vigorous cell-mediated immune response growth was fully inhibited. A similar but less extensive effect on M. leprae viability was observed in response to the local injection of 5 units in 0.1 ml of purified protein derivative of tuberculin (PPD). -Authors' Abstract
Deshpande, R. G., Khan, M. B. and Navalkar, R. G. Immunoreactivity of a mammalian liver component with leprosy sera. Int. Arch. Allergy Appl. Immunol. 97(1992)345-349.
Sera from 77 leprosy patients in various stages of infection -tuberculoid (TT), lepromatous (LL), borderline tuberculoid and borderline lepromatous- 15 contacts, and 21 normal healthy individuals were assayed in an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and dot enzyme immunoassay using ethanol-soluble and thermostable extract of liver as the antigen. The highest incidences of reaction were found in untreated LL patients (100%) and in TT patients (91%), while the sera from borderline patients showed a comparatively lower incidence (43%). Some of the sera from contacts of leprosy patients (6/15) also showed high reactivity. Assays using lecithin as an antigen did not exhibit any reaction. -Authors' Abstract
DeSousa, J. P. C., Bachelet, M. and Rastogi, N. Effect of indomethacin on the modulation of Mycobacterium avium growth in human macrophages by interferon gamma, retinoic acid and l,25(OH)2-vitamin-D3. FEMS Microbiol. Immunol. 89(1992)281-286.
A virulent strain of Mycobacterium avium was grown actively inside human, adherent, peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages with enhanced synthesis of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). We therefore decided to investigate if the inability of human macrophages to control M. avium infection could be reversed using various immunomodulators, i.e., retinoic acid (RA), 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D3 (D3) and interferon gamma (IFN-gamma) alone or in combination, and whether this reversal was further potentiated by the addition of indomethacin (IND), a potent inhibitor of PGE2 biosynthesis. Among the various immunomodulators employed, only RA alone or in association with D3 or both D3 and IFNgamma were able to produce a clear mycobacteriostatic effect, which was further potentiated by IND. Our data suggest that immunosuppressive pathways induced in macrophages infected by M. avium result partly from an increased synthesis of PGE2 occurring soon after infection. -Authors' Abstract
Elsaghier, A., Prantera, C., Bothamley, G., Wilkins, E., Jindal, S. and Ivanyi, J. Disease association of antibodies to human and mycobacterial hsp70 and hsp60 stress proteins. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 89(1992)305-309.
Structural homology between microbial and human stress proteins has been postulated to be a basis for autoimmunization in chronic inflammatory diseases. Therefore, we estimated by ELISA titration the antibody levels to mycobacterial (M) and human (H) recombinant hsp 70 and M-hsp65 heat-shock proteins in sera of patients with Crohn's disease (N = 29), ulcerative colitis (N = 20) and nontuberculous mycobacterial disease of the lungs (N = 20). Antibodies to H-hsp60, separated by twodimensional gel electrophoresis, were tested in six sera of each group of patients. In Crohn's disease, antibody titers to the M-hsp65 antigen without detectable H-hsp60 binding were significantly elevated in 52% of the patients. In contrast titers to both M-hsp70 and H-hsp70 were demonstrable and correlated, but increased over control values only in four (14%) patients. The antibody pattern in ulcerative colitis was found to be quite different: anti-H-hsp60 binding was demonstrable in most patients, although anti-M-hsp65 titers were not elevated. Furthermore, 25% of patients had significantly elevated titers to M-hsp70, but not to H-hsp70. In nontuberculous mycobacterial pulmonary disease, about 50% of patients had elevated titers to both hsp65 and hsp71 mycobacterial antigens but not to the corresponding human proteins; patients with Mycobacterium xenopi infection had the highest titers in this group. These results demonstrate the existence of distinct disease-associated patterns in the human antibody response to stress protein antigens. However, these data are not sufficient to imply sensitization with mycobacteria in patients with inflammatory bowel diseases, since certain epitopes of heat-shock proteins are shared by several bacterial genera. -Authors' Abstract
Godfrey, H. P., Feng, Z. H., Mandy, S., Mandy, K., Huygen, K., Debruyn, J., Abou-Zeid, C, VViker, H. G., Nagai, S. and Tasaka, H. Modulation of expression of delayed hypersensitivity by mycobacterial antigen-85 libronectin-binding proteins. Infect. Immun. 60(1992)2522-2528.
Although demonstration of delayed hypersensitivity to purified protein derivative of tuberculin (PPD) is an important clement in the diagnosis of infection with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, many patients with tuberculosis are anergic. Several possible mechanisms for this specific lack of response have been described. We have now uncovered an additional one. T-cell fibronectin (FN), a lymphokinc secreted by activated T cells, is closely associated with the initiation of delayed hypersensitivity reactions. Mycobacterial antigen 85 (Ag85) proteins have been shown to bind to plasma FN. The ability of Ag85 to bind to T-cell FN and modulate expression of delayed hypersensitivity was therefore studied. Purified Ag85 proteins from M. tuberculosis, M. bovis BCG, or M. kansasii bound to T-cell FN, fibroblast FN, and plasma FN in vitro. Purified 65-kDa heat-shock protein (hsp65) from M. bovis BCG did not bind to any FN. Ag85, but not hsp65, inhibited the ability of T-cell FN to agglutinate monocytes in vitro in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo, mixtures of PPD or dinitrophenyl-ovalbumin and purified M. tuberculosis or M. bovis BCG Ag85 proteins elicited significantly smaller delayed hypersensitivity inflammatory reactions in sensitized guinea pigs than did PPD or dinitrophenyl-ovalbumin alone. Purified hsp65 did not inhibit expression of delayed hypersensitivity to PPD or dinitrophenyl-ovalbumin. We suggest that Ag85 proteins could inhibit in vivo expression of delayed hypersensitivity during mycobacterial infections because of their interaction with T-cell FN.-Authors' Abstract
Hacker, F., Kromer, S., Heeg, K., Ivanyi, J., Wagner, H. and Pfeffer, K. Opportunist mycobacteria express ligands that stimulate production of human V-gamma-9V-delta-2 lymphocytes-T. Infect. Immun. 60(1992)2753-2757.
Human gamma-delta-T cells are known to respond at high frequencies to pathogenic mycobacteria. Here we show that opportunistic strains of mycobacteria share with pathogenic mycobacteria the ability to trigger at high frequencies human V-gamma9V-delta-2 T-cell-receptor positive T lymphocytes. Stimulating ligands were present in part in a low-molecular-weight fraction of lysates from opportunistic mycobacteria, as has been found for pathogenic strains. These results support the view that postnatal exposure to ever-present opportunistic mycobacteria may be a driving force for the numerical expansion of the V-gamma9V-delta-2 T-cell subset in adolescence - Authors' Abstract
Hajeer, A. H., Worthington, J., Morgan, K. and Bernstein, R. M. Monoclonal antibody epitopes of mycobacterial 65-kD heat-shock protein defined by epitope scanning. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 89(1992)115-119.
The binding sites for monoclonal antibodies (MoAbs) to the 65-kDa heat-shock protein (hsp65) of mycobacteria have been investigated by epitope scanning. Five hundred and twenty-six 8-mer peptides representing the complete sequence of Mycobacterium tuberculosis hsp65 were synthesized in duplicate using the Epitope Scanning Kit (CRB Ltd.). The epitopes of six MoAbs raised to the hsp65 of M tuberculosis or M. leprae were investigated. We have identified the epitope of a new MoAb (DC 16); this epitope is continuous, hydrophilic in nature, and 11 amino acids long. We have also confirmed the location of the epitopes of three MoAbs (IIH9, ML30 and IIC8). Thus, the epitope scanning technique has proved suitable for the detection of continuous epitopes of hsp65.-Authors' Abstract
Heifets, L. B., Lindholm-Levy, P. J. and Comstock, R. D. Bacteriostatic and bactericidal activities of gentamicin alone and in combination with clarithromycin against Mycobacterium avium. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36(1992)1695-1698.
The inhibitory activity of gentamicin against Mycobacterium avium depended on the pH of the medium, and the broth-determined MICs for 90% of strains were 5.0 µg/ml at pH 7.4, 9.5-µg/ml at pH 6.8, and > 16.0-µg/ml at pH 5.0. The MBCs were two- to eightfold higher than the MICs. The combined effect of gentamicin and clarithromycin was additive, and the MICs and MBCs of each drug were either the same as those in the single-drug tests or reduced twofold.-Authors' Abstract
Hussain, R., Jamil, S., Dockrell, H. M., Chaing, T. J. and Hasan, R. Detection of high titres of Toxoplasma gondii antibodies in sera of patients with leprosy in Pakistan. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 86(1992)259-262.
Untreated and treated leprosy patients and their household contacts were screened for antibody to Toxoplasma gondii using antigen-coated latex particles. A significantly high level of seroprevalence (29.6%) was observed in the untreated leprosy patients compared to endemic controls (p < 0.01) with a mean reciprocal antibody titer of 20,007 ± 3580 (N = 98) in seropositive patients. In treated patients seroprevalence dropped to 13.5%. Seroprevalence in a group of household contacts of leprosy patients was similar to that of control subjects from an endemic area but not exposed to leprosy (7.8% and 6.1%, respectively), indicating that the increased seroprevalence in leprosy patients was not merely due to increased exposure related to socioeconomic factors. Antigenic crossreactivity between T. gondii and Mycobacterium leprae antigens was ruled out by cross-inhibition experiments carried out with soluble antigens from each of the organisms. We believe these antibodies may be induced by an increase in T. gondii load in leprosy due to a transient reactivation of latent T. gondii infections, as the antibodies in these leprosy patients were not associated with any sign of eye or lymphatic pathology related to toxoplasmosis.-Authors' Abstract
Mistry, Y., Young, D. B. and Mukherjee, R. Hsp70 synthesis in Schwann cells in response to heat shock and infection with Mycobacterium leprae. Infect. Immun. 60(1992)3105-3110.
Induction of heat-shock protein synthesis was monitored in murine and monkey Schwann cells exposed to elevated temperatures. Synthesis of the stress-inducible 70kDa heat-shock protein (hsp70) was detected in both murine and primate Schwann cells by metabolic labeling and by inimunoblotting with a specific monoclonal antibody. Hsp70 synthesis was also induced in Schwann cells after infection with Mycobacterium leprae and was detected from 24 hr to 1 week postinfection. These results are discussed with respect to the possible role of heat-shock proteins in immunopathological events associated with the clinical manifestations of leprosy. -Authors' Abstract
Pancholi, P., Steinman, R. M. and Bhardwaj, N. Dendritic cells efficiently immunosclect mycobacterial-reactive T-cells in human blood, including clonable antigenreactive precursors. Immunology 76(1992)217-224.
Given the persistence of tuberculosis throughout the world, the delineation of mechanisms that lead to protective immunity to Mycobacterium tuberculosis is important. We have evaluated the presenting function of human dendritic cells for mycobacterial antigens, since these antigenpresenting cells (APC) are particularly effective in initiating antigen-specific T-cell responses. Dendritic cells from blood prove to be active APC for mycobacteria-specific proliferative responses by CD4+ T cells from bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG)-vaccinated individuals. In the first 24 hr-48 hr of the response, dendritic cells that have been pulsed with mycobacterial antigens, including live BCG, effectively bind T cells forming discrete cell clusters. The clusters represent about 1% of the applied T cells. Clusters are highly enriched in mycobacterial reactivity while the nonclusters are depleted. Clustered T cells can be used as a starting point to expand antigen-specific cell lines. Mitogen and allogeneic feeder cells were used as APC to expand the mycobacterial-reactive lines because the antigenspecific T cells had been preselected by virtue of their binding to antigen-pulsed dendritic cells. We discuss the advantages of obtaining antigen-reactive T cells by using dendritic cells as immunoadsorbents. These lines should help delineate the range of mycobacterial antigens and T-cell responses that participate in host responses to mycobacteria. -Authors' Abstract
Quayle, A. J., Wilson, K. B., Li, S. G., Kjeldsenkragh, J., Oftung, E., Shinnick, T., Sioud, M., Forre, O., Capra, J. D. and Natvig, J. B. Peptide recognition, T-cell receptor usage and HLA restriction elements of human heat-shock protein (hsp) 60 and mycobacterial 65-kDa hsp-reactive T-cell clones from rheumatoid synovial fluid. Eur. J. Immunol. 22(1992)1315-1322.
A commonly held postulate regarding the etiology of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is that of antigenic mimicry. Recent interest has focused on the mycobacterial 65-kDa heatshock protein (hsp) as a putative causal agent. The 65-kDa hsp has over 40% sequence homology with the human hsp60. and elevated synovial T-cell responses to both antigens have been demonstrated in RA and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis patients. Such T cells should, therefore, be specific for shared epitopes on the two antigens. To investigate this, we screened synovial fluid mononuclear cells from two early RA patients with peptides of the 65-kDa hsp which have the greatest homology with the human hsp60. We also raised a panel of T-cell clones from one of the patients with the 65-kDa hsp. The synovial T-cell population from both patients and one of the T-cell clones recognized a peptide representing the amino-acid sequence 241-255. This clone also responded to the peptide of the equivalent human sequence, and was restricted by HLA-DQ. A second T-cell clone recognized an adjacent epitope (amino acid sequence 251-265) which is also highly homologous with the human sequence, but this clone was restricted by HLA-DR. The clones utilized different V(beta) gene segments but the same D(beta) and J(beta) gene elements, and both exhibited specific cytotoxicity against autologous antigen-pulsed macrophages. Our findings, therefore, do not disagree with the postulate that autoimmune disease could possibly be triggered by bacterial epitopes with homology to self protein. However, it is also noted that there are alternative interpretations of these data. -Authors' Abstract
Rambukkana, A., Das, P. K., Krieg, S. and Faber, W. R. Association of the mycobacterial 30-kDa region proteins with the cutaneous infiltrates of leprosy lesionsevidence for the involvement of the major mycobacterial secreted proteins in the local immune response of leprosy. Scand. J. Immunol. 36(1992)35-48.
The granulomatous skin lesions of human leprosy are known to be due to the cutaneous immune reaction to various mycobacterial antigens. In the present study, by immunohistochemical analysis using a previously characterized monoclonal antibody (MoAb) 3A8, we have demonstrated a selective expression of the 3A8 epitope of mycobacterial 30-kDa proteins, the major secreted proteins of mycobacteria in various forms of leprosy lesions across the clinical spectrum. The localization of MoAb 3A8 staining is confined to the areas of cellular infiltrates of the lesions. In tuberculoid lesions the intense 3A8 staining was seen mostly in association with the membrane of the dermal cellular infiltrates; whereas in highly bacilliferous lepromatous lesions the staining seems to be diffused with granular appearance but not in the form of bacteria. In patients with reversal reaction the staining was specifically extended to cells infiltrating the epidermis. MoAb 3A8 did not show any reactivity with inflammatory skin lesions of patients other than those with leprosy. Since the 3A8 epitope of 30-kDa proteins has been shown to be present in all cellular compartments of the mycobacteria and in the actively secreted BCG 85 antigen complex, MoAb 3A8 reactive protein(s) in leprosy lesions may be derived cither from degraded somatic mycobacterial products or from antigens actively secreted by live bacilli. The latter could be true in the cases of untreated lepromatous lesions with high bacterial load since live Mycobacterium leprae has also been considered to secrete corresponding 30-kDa proteins similar to other closely related mycobacteria. By double immunoenzyme staining we clearly demonstrate the expression of 3A8 epitope on CD68+ macrophages in the granulomas of tuberculoid leprosy; whereas in highly bacilliferous lepromatous lesions most of the double staining was seen in a diffuse pattern within the interstitial space of the cellular infiltrate as well as in the cytoplasm of CD68+ macrophages. In lesions from reversal reaction the 3A8 epitope is more strongly expressed on CDla + dendritic Langerhans' cells (LC), both in the epidermis and in the dermis as compared with other types of leprosy. This provides evidence for the involvement of LC in the handling of mycobacterial antigenic epitopes in leprosy lesions. Further, immunoenzyme double staining revealed that the expression of this mycobacterial 3A8 epitope on antigen-presenting cells, such as CD68+ macrophages and CDla + LC, is present in juxtaposition with CD3+ T cells including the alpha-beta and gamma-delta-receptorbearing T cells in the granuloma. Our results suggest that 3A8 may be a potential T-cell epitope that could be involved in the local tissue immune response of leprosy. -Authors' Abstract
Rastogi, N., Bachelet, M. and Desousa, J. P. C. Intracellular growth of Mycobacterium avium in human macrophages is linked to the increase synthesis of prostaglandin E2 and inhibition of the phagosome-lysosome fusions. FEMS Microbiol. Immunol. 89(1992)273-279.
A virulent strain of Mycobacterium avium grew actively inside human, adherent peripheral blood monocyte-derived macrophages. Bacteria were always confined to the phagosome compartment and were encapsulated. Cytochemical labeling of acid phosphatase using transmission electron microscopy showed a strong inhibition of the phagosome-lysosome fusions (PLF) in macrophages since not more than 25%-30% bacteria containing phagosome at any time effectively fused with lysosomes. In case of a positive fusion event, the bacterial capsule prevented the diffusion of the lysosomal contents to the bacterial surface. Moreover, the infection of macrophages both by living and gamma-irradiation-killed M. avium was linked to an increased synthesis of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2); however the total amount of PGE2 synthesized in the latter case was significantly lower than that observed with viable organisms. Our results suggest that the inability of human macrophages to control M. avium infection is linked to immunosuppressive pathways, e.g., enhanced synthesis of PGE2, and also to an impairment of normal microbicidal functions of the infected macrophages.- Authors' Abstract
Roche, P. W., Neupane, K. D. and Britton, W. J. Cellular immune response to the cell walls of Mycobacterium leprae in leprosy patients and healthy subjects exposed to leprosy. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 89(1992)110-114.
Cell walls of Mycobacterium leprae consist of complex arrangements of carbohydrate, lipid, peptidoglycan, and protein molecules. Recently, extractable proteins of a wide range of molecular weights were identified as components of the cell -wall. We have examined the cellular-immune responses of Nepali leprosy patients to a cellwall preparation of M. leprae enriched for these proteins. Strong lymphocyte proliferative responses to the antigens were present in half of the paucibacillary leprosy patients and in the majority of healthy control subjects with occupational exposure to leprosy. Patients with multibacillary disease responded poorly, and patients with tuberculosis had intermediate responses. Proliferative responses to the cell-wall protein fraction were strongly correlated to the proliferative responses to sonicates of the whole leprosy bacillus. Immunization of mice with cell-wall proteins resulted in inhibition of growth of M. leprae following foot pad inoculation with viable organisms. Therefore cell-mediated immune responses to the extractable proteins of the cell wall may play a role in protective immunity against M. leprae infection.-Authors' Abstract
Sahu, A., Saha, K., Mukherjee, A. and Sehgal, V. N. In vivo effects of anti-leprosy drugs on the rat peritoneal macrophages and lymphocyte subpopulations. Int. J. Immunopharmacol. 14(1992)721.
The present study describes the in vivo effects of antileprosy drugs on rat peritoneal macrophages and T-cell homeostasis. It was observed that BCG-elicited, rat peritoneal macrophages produced more H2O2 and expressed more la antigen on their cell surfaces compared with resident peritoneal macrophages. Furthermore, elicited macrophages isolated from rats administered multidrug therapy (MDT), consisting of dapsone, clofazimine and rifampin in high dose (10 × MDT) released more O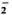 . On the contrary, there was a significant decrease in the la-antigen expression on these macrophages. Antileprosy drug treatment in high dose (10 × MDT) decreased the total number of blood T-helper (W3/25 + ) cells and increased the total number of blood T-suppressor (OX-8+) cells which resulted in a significant decrease in a W3/25:OX-8 ratio. Electron microscopy of elicited macrophages isolated from 10 × MDT-treated rats showed development of many filipodia compared with control macrophages. These data show that 10 × MDT treatment in rats for 1 month alters the homeostasis of blood T-cell subpopulations which perhaps decreases the la expression on macrophages. However, the increase in O
. On the contrary, there was a significant decrease in the la-antigen expression on these macrophages. Antileprosy drug treatment in high dose (10 × MDT) decreased the total number of blood T-helper (W3/25 + ) cells and increased the total number of blood T-suppressor (OX-8+) cells which resulted in a significant decrease in a W3/25:OX-8 ratio. Electron microscopy of elicited macrophages isolated from 10 × MDT-treated rats showed development of many filipodia compared with control macrophages. These data show that 10 × MDT treatment in rats for 1 month alters the homeostasis of blood T-cell subpopulations which perhaps decreases the la expression on macrophages. However, the increase in O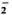 production and the appearance of filipodia on the macrophages is due to a direct effect of drugs on the macrophages. MDT treatment for 1 month in a therapeutic dose has no effect on the above-mentioned parameters.-Authors' Abstract
production and the appearance of filipodia on the macrophages is due to a direct effect of drugs on the macrophages. MDT treatment for 1 month in a therapeutic dose has no effect on the above-mentioned parameters.-Authors' Abstract
Sampaio, E. P., Moreira, A. L., Sarno, E. N., Malta, A. M. and Kaplan, G. Prolonged treatment with recombinant interferon-gamma induces erythema nodosum leprosum in lepromatous leprosy patients. J. Exp. Med. 175(1992)1729-1737.
Ten patients with borderline and lepromatous leprosy were selected for a prolonged trial with recombinant interferongamma (rIFN-gamma). Patients received 30-µg intradermally for six injections over a 9-day period, and then cither 100-µg intradermally every 1 mo for 10 mo or every 2 wk for 5 mo (total, 1.2 nig). Erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL) was induced in 60% of the patients within 6-7 mo, as compared with an incidence of 15% per year with multiple drug therapy alone. The mean whole-body reduction in bacterial index over the first 6 mo was 0.9 log units. Cutaneous induration at the intradermal injection sites of > 15 mm predicted the development of a subsequent rcactional state. Monocytes obtained from patients receiving the lymphokine demonstrated an increased respiratory burst and a 2.5-5.1-fold increase in tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) secretion in response to agonists. Patients in ENL had an even higher release of TNFalpha from monocytes as well as high levels of TNF-alpha in the plasma (mean, 2000 pg/ml). Thalidomide therapy was required to treat the systemic manifestations of ENL. Control of toxic symptoms with thalidomide was associated with a 50%-80% reduction in agonist-stimulated monocyte TNF-alpha secretion. IFN-gamma enhanced the monocyte release of TNF-alpha by 3-7.5-fold (agonist dependent) when added to patients' cells in vitro, and this could be suppressed by the in vitro addition of 10-µg/ml of thalidomide. -Authors' Abstract
Sasiain, M. D., Delabarrera, S., Minnucci, F., Valdez, R., DeBracco, M. M. D. and Balina, L. M. T-cell mediated cytotoxicity against mycobacterium antigenpulsed autologous macrophages in leprosy patients. Infect. Immun. 60(1992)3389-3395.
The involvement of CD4+ T lymphocytes in the defense mechanisms against intracellular pathogens is widely recognized. Little information is available on the generation and specificity of the cytotoxic cells that eliminate human monocytes/macrophages infected with mycobacteria. In this work, we tested whether mononuclear cells from leprosy patients could generate cytotoxic T-cell activity against autologous macrophages pulsed with Mycobacterium leprae or purified protein derivative (PPD) in a 4-hr Cr-51 release assay. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from normal M. bovis BCG-immunized controls or from leprosy patients stimulated with antigen for 7 days were used as effector cells. Paucibacillary (PB) patients and normal controls yielded more active effector cells in this system than multibacillary (MB) patients. MB patients were able to develop cytotoxicity against M. leprae, BCG, or PPD, in contrast with the immunological anergy widely described. We did not find cytotoxicity against unpulsed macrophages. Crossreactivity was observed between PPD, BCG, and M. leprae. Only antigen-pulsed autologous macrophages were suitable as target cells. M. leprae-induced cytotoxic cells were found in both CD4+ CD8- and CD4- CD8 + T-cell subsets; whereas CD4+ cells were the main component of PPD-induced cytotoxicity. In MB patients, BCG-induced cytotoxic cells were better killers of M. leprae pulsed macrophages than cells induced by M. leprae. This is an interesting finding in view of the ongoing vaccination trials. The involvement of CD4- or CD8-mediated cytotoxicity may be important in the balance between protection and tissue or nerve damage.-Authors' Abstract
Shu, H.-W., et al. [A study of subclinical infection with M. leprae. (IV) The result of follow-up over three years of the household contacts with leprosy.] China Lepr. J. 7(1991)211-214. (in Chinese)
The household contacts of leprosy patients have been followed over 3 years with PGI-ELISA. At the beginning, there were 76 persons with suspected positivity, 75 with positivity, and 3 with strong positivity. When re-examined at the third year, among the 76 cases with suspected positivity, 40 cases have become negative (52.6%) and 33 become positive (43.4%); among the 75 cases with positivity, 12 have become suspect, 33 negative (44%) and 5 cases have increased the degree of positivity (6.7%), and among the 5 cases with stronger positivity there was not any case turned negative. In those who had been positive at the beginning, one person was diagnosed as BT leprosy in the second year when he was 15 years old. It seems that the follow up of the household contacts with PGI-ELISA could contribute to finding patients with early leprosy.-Authors' English Abstract
Stanford, J. L. Improving on BCG. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Immunol. Scand. 99(1991)103-113.
BCG is the only vaccine for tuberculosis and leprosy known to be effective in at least some places. Unfortunately it tends to be less successful in just those areas of the developing world where a vaccine is most needed. Although molecular biology offers the prospect of alternatives, these still lie in the indefinite future, and the best use has to be made of BCG. A number of preparations are available from different manufacturers, and a vaccine should be selected with good evidence of efficacy, and a low incidence of complications. Selection of the optimal age for administering BCG should be based on factors pertaining in the area where it is to be used. The influence of contact with environmental mycobacteria, the age at which mycobacterial diseases occur, and the logistics of vaccine delivery must be taken into account. The addition of a suspension of killed Mycobacterium vaccae to BCG may increase its efficacy. Skin-test data show that recognition of antigens common to all mycobacterial species and thought to be the first step in the protective immune response, is significantly enhanced by the additive. M. vaccae also contains a substance, or substances, "switching off' the tissue destructive aspect of the Koch phenomenon that is part of the immunopathology of tuberculosis. A suspension of killed M. vaccae alone can be used to enhance immune responses of persons unsuitable for BCG vaccination, such as those already tuberculin positive, and those with scars of earlier BCG vaccination.-Author's Summary
Tin-Shwe and Pe-Than-Myint. Lepromin reaction in patients with falciparum malaria. Myanmar Health Sci. Res. J. 2(1990)157-159.
Over half (57.7%) of 116 malaria patients (aged 12-65 years) gave a negative or doubtful Mitsuda reaction to intradermal lepromin compared with only 7% of 100 control contacts of the malaria patients. For the malaria patients, there was no significant correlation between the intensity of the lepromin reaction and the density of the malaria parasites or the clinical category of the malaria. The negative reaction to the leprosy bacillus antigen is presumed to be due to immunodepression during the active phase of malaria. -C. A. Brown (Trop. Dis. Bull.)
Van Vooren, J. P., Drowart, A., DeBruyn, J., Launois, P., Millan, J., Delaporte, E., Develoux, M., Yernault, J. C. and Huygen, K. Humoral responses against the 85 A and 85B antigens of Mycobacterium bovis BCG in patients with leprosy and tuberculosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30(1992)1608-1610.
Immunoglobulin G antibodies against the 85 A and 85B components of the Mycobacterium bovis BCG antigen 85 complex separated by isoelectric focusing were investigated in scrum samples from 129 patients representing the major forms of leprosy, 111 tuberculous patients, and 153 healthy subjects. For both of the antigens, a higher degree of staining was observed for lepromatous leprosy patients and patients with active tuberculosis than for the other groups. Because sera from some healthy subjects recognized the 85A antigen, we suggest that antigen 85B is the most useful component of the antigen 85 complex for the serodiagnosis of the multibacillary forms of leprosy or of the active forms of tuberculosis. - Authors' Abstract
Villarreal-Ramos, B., Sanchez-Garcia, J., Stoker, N., et al. Screening gene expression libraries for epitopes recognized in Mycobacterium leprae by mouse T cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 21(1991)2621-2624.
Parasite expression libraries have so far been screened with antibodies, DNA probes or T-cell clones. Immunity to many parasites, such as Mycobacterium leprae, is largely mediated by T cells, and so the screening of such libraries for T-cell epitopes is an important step toward the development of effective vaccines and diagnostic reagents. A new method for screening of λgtl 1 libraries with uncloned T-cell populations is presented here, which takes advantage of the fact that the recombinant proteins contain β-galactosidase as their leader peptide; this allows them to be semipurified by means of anti-β-galactosidase antibodies coated on the bottom of microliter plate wells, within which a proliferation assay can then be carried out. Optimum conditions for the assay were determined, using the M. leprae 18-kDa antigen as a test antigen. -Authors' Abstract
Ye, F., et al. [Immunohistochemical study of leprosy skin lesions using S-100 protein and α-antichymotrypsin.] China lepr. J. 8(1992)19-20. (in Chinese)
Skin biopsies of 24 patients with leprosy, including LL 7, BB 4, TT 11, BT 1 and I 1, were studied by using S-100 protein and α-antichymotrypsin (AACT) immunohistochemical methods. A few Langerhans' cells were seen in lesions of the dermis, especially in lepromatous leprosy, indicating that the cellular immunity induced by Langerhans' cells is reduced. By using AACT, most of the epithelioid cells, multinucleate giant cells and macrophages in the lesions of tuberculoid leprosy were positive, but most of the foamy cells in the lesions of lepromatous leprosy were negative. Moreover, the negative result of S-100 protein binding to the nerves in the lesions is helpful in differentiating leprosy from tuberculosis and sarcoidosis.-Authors' English Abstract
MICROBIOLOGY
Alugupalli, S., Mielniczuk, Z. and Larssen, L. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry methods for analysis of secondary alcohols present in the Mycobacteriumavium complex. J. Microbiol. Methods 15(1992)229-240.
Secondary alcohols of mycobacteria belonging to the Mycobacterium avium complex were studied by gas chromatography and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. After hydrolysis of the mycobacterial cells followed by extraction of the alcohols, trimethylsilyl, trifiuoroacetyl, heptafluorobutyryl and pentafluorobenzoyl derivatives were formed. In the electron impact mode the trimethylsilyl derivative of 2-eicosanol was detected down to 10 pg; whereas in the negative ion chemical ionization mode the pentafluorobenzoyl derivative was detected at the 1 pg level. An alcohol not previously detected in mycobacteria was found in all of the studied strains; it was identified as 2-nonadecanol. The methods described may be useful for the detection of certain mycobacteria, including the M. avium complex, in clinical or environmental samples.-Authors' Abstract
Arnoldi, J., Schluter, C, Duchrow, M., Hubner, L., Ernst, M., Teske, A., Flad, H. D., Gerdes, J. and Bottger, E. C. Species-specific assessment of Mycobacterium leprae in skin biopsies by in situ hybridization and polymerase chain reaction. Lab. Invest. 66(1992)618-623.
Conventional histopathologic diagnosis of mycobacterial infections are limited to the determination of "acid-fast bacilli." A species-specific diagnosis is thus far impossible. In addition, routine microbiologic assessments of mycobacteria suffer from the major drawback that a species-specific diagnosis is extremely time consuming and in several cases even impossible. As Mycobacterium leprae cannot be cultured in vitro, we tried to specifically target this obligate intracellular parasite by in situ hybridization and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques. For this purpose we used a 22 mer oligonucleotide probe recognizing a species-specific sequence of the 16S rRNA of M. leprae. Using an immunoenzymatic detection method for in situ hybridization we were able to specifically assess M. leprae a) in long-term cultured macrophages in vitro infected with different mycobacteria species and b) in frozen sections of skin biopsies obtained from patients suffering from lepromatous leprosy. These results could be confirmed and extended by PCR experiments in which we used conserved oligonucleotide primers for 16S rRNA to amplify bacterial DNA isolated from different eubacterial species and from fresh-frozen as well as from formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded and routinely processed mycobacteria-infected tissues. Upon Southern blot analysis, the M. leprae-specific oligonucleotide probe exclusively hybridized with PCR products obtained from M. leprae-conten-ing samples (including paraffin sections), but not with PCR products obtained from samples containing other mycobacterial species. As species-specific oligonucleotide probes targeted at rRNA are described for a variety of mycobacterial species, these methods may be generally applied for a rapid species-specific assessment of mycobacteria in histologic material. -Authors' Abstract
Basu, J., Chattopadhyay, R., Kundu, M. and Chakrabarti, P. Purification and partial characterization of a penicillin-binding protein from Mycobacterium smegmatis. J. Bacteriol. 174(1992)4829-4832.
Penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs), although characterized from several organisms, have so far not been studied in mycobacteria. The present study is the first characterization of a PBP from Mycobacterium smegmatis. The PBP was purified by solubilization of the membranes with Triton X-100 and successive chromatography of the solubilized proteins on ampicillinlinked CH Sepharose 4B and DE-52. The purified PBP (M(r), 49,500) catalyzed a model transpeptidase reaction with the tripeptide acety12-L-Lys-D-Ala-D-Ala as the substrate and Gly-Gly as the acceptor. The transpeptidase activity was inhibited by 50% at a benzylpenicillin concentration of 1.8 × 10 -7 M, which was similar to the concentration (1.1 × 10-7 M) of benzylpenicillin required to saturate to 50% this PBP. Of several antibiotics tested, the concentration of antibiotic required to inhibit [S35]penicillin binding by 90% was found to be the lowest for cefoxitin and Sch 34343. - Authors' Abstract
Dewit, T. F. R., Bekelie, S., Osland, A., Miko, T. L., Hermans, P. W. M., Vansoolingen, D., Drijfhout, J. W., Schoningh, R., Janson, A. A. M. and Thole, J. E. R. Mycobacteria contain two groEL genes-the second Mycobacterium leprae groEL gene is arranged in an operon with groES. Mol. Microbiol. 6(1992)1995-2007.
In contrast to other bacterial species, mycobacteria were thus far considered to contain groEL and groES genes that are present on separate loci on their chromosomes. Here, by screening a Mycobacterium leprae lambda gtl 1 expression library with serum from an Ethiopian lepromatous leprosy patient, two DNA clones were isolated that contain a groEL gene arranged in an operon with a groES gene. The complete DNA sequence of this groESL operon was determined. The predicted amino-acid sequences of the GroES and GroEL proteins encoded by this operon are 85%-90% and 59%-61% homologous to the sequences from previously characterized mycobacterial GroES-and GroEL proteins. Southern blotting analyses with M. leprae groES- and groEL-specific probes demonstrate that similar groESL homologous DNA is present in the genomes of other mycobacteria, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This strongly suggests that mycobacteria contain a groESL operon in addition to a separately arranged second groEL gene. Using five T-cell clones from two leprosy patients as probes, expression of the M. leprae GroES protein in Escherichia coli after heat shock was demonstrated. Four of these clones recognized the same M. /cprac-specific GroESderived peptide in a DR2-restricted fashion. No expression of the groEL gene from this operon was detected in E. coli after heat shock, as tested with a panel of T-cell clones and monoclonal antibodies reactive to previously described GroEL proteins of mycobacteria.-Authors' Abstract
Kempsell, K. E., Ji, Y.-E., Estrada-G., I. C. E. and Colston, M. J. The nucleotide sequence of the promoter, 16S rRNA and spacer region of the ribosomal RNA operon of Mycobacterium tuberculosis and comparison with Mycobacterium leprae precursor rRNA. J. Gen. Microbiol. 138(1992)1717-1727.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Rv has a single rrn (ribosomal RNA) operon. The operon was cloned and a region of 1536 nucleotides was sequenced, starting 621 bp upstream from the 5'-end of the 16S rRNA coding region and continuing to the start of the 23S rRNA coding region. The 16S rRNA sequence inferred from the gene sequence was found to differ in one position from M. bovis (nucleotide 1443) and from M. microti (nucleotide 427). A single putative promoter was identified on the basis of similarities with the sequence of rrn operons of Bacillus subtilis and Escherichia coli. The regions of similarity include a -35 box, a - 10 box, a stringent response element, antitermination signals, potential RNAase III processing sites and features of precursor rRNA secondary structure. Sequences upstream from the 5'-end of M. leprae 16S rRNA were also investigated. Homologous schemes of secondary structure were deduced for precursor rRNA of both M. tuberculosis and M. leprae; although the principal features are common to both species there are notable differences. -Authors' Abstract
Quemard, A., Laneelle, G., and Lacave, C. Mycolic acid synthesis -a target for ethionamide in mycobacteria. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36(1992)1316-1321.
Striking structural analogies exist between the two specific antimycobacterial drugs ethionamide (ETH) and isoniazid (INH), and they share several inhibitory properties in susceptible species of mycobacteria. The effect of ETH on mycolic acid synthesis was studied in whole cells and in cell extracts of various species, since this synthesis is one direct target for INH, as we recently demonstrated in cell extracts of Mycobacterium aurum. It was shown in the present study that there is not a direct relationship between ETH susceptibility and mycolic acid inhibition. This observation could explain the lack of cross-resistance between the two drugs. The presence of ETH disturbed mycolic acid synthesis in both resistant and susceptible mycobacteria. Synthesis of oxygenated species of mycolic acid was inhibited, while that of diunsaturated acids was either slightly altered or even increased. In contrast, INH inhibited the synthesis of all kinds of mycolic acids in the same way in all susceptible strains and had no effect on mycolic acid synthesis in resistant strains. In the presence of ETH, the unsaturated mycolic acid molecules presented a methyl end different from the usual one. These data strongly suggest that the normal unsaturated mycolic acid species are not the precursors of the oxygenated types. Moreover, they show that ETH probably acts early in the pathway leading to oxygenated mycolic acid.-Authors' Abstract
Rastogi, N., Labrousse, V. and Barreau, C. A rapid microbcad method for breaking pathogenic mycobacteria -application in SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis. Curr. Microbiol. 24 (1992) 311-317.
A rapid method used to obtain cell-free extracts from pathogenic mycobacteria was successfully applied to five slowly growing species. The method, which simply consisted of vortexing of the bacterial suspensions with 130-µm glass microbcads under predefined conditions, resulted in the breaking of bacterial cells as evidenced by electron microscopy and gave about 1 mg/ml of total proteins. The cell-free extracts so obtained were suitable for SDS-PAGE analysis as well as Western blots. In a pilot test system, this method was applied to Mycobacterium avium, M. paratuberculosis, and related species isolated from "woodpigeon" (M. silvaticum) and Crohn's disease. The procedure was used in the analysis of various mycobacterial proteins by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting, and the findings were compatible with recently published data using criteria based on DNA polymorphism and numerical taxonomy. -Authors' Abstract
Santos, A. R., De Miranda, A. B., Lima, L. M., Suffys, P. N. and Degrave, W. M. Method for high yield preparation in large and small scale of nucleic acids from mycobacteria. J. Microbiol. Meth. 15(1992)83-94.
A simple and very straightforward method for the extraction, in both large scale and micro scale, of high molecular weight DNA and RNA from mycobacteria is described. The method requires few manipulations, is independent of previous mycobacterial culture conditions, and is extremely efficient, yielding nucleic acids of very high quality which allowed the construction of genomic libraries of Mycobacterium leprae, M. tuberculosis and M. bovis BCG. The influence of several variables, such as mechanical treatment and chemicals, used is discussed.-Authors' Abstract
Smid, I., Salfinger, M. and Vurmarapp, U. The use of radiometric tests in the speciation of mycobacteria-a review. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. [A] 276(1992)493-501.
Besides a more rapid detection and susceptibility testing, radiometry offers possibilities for the identification of mycobacteria. This paper gives a chronological summary of radiometric techniques used in the BACTEC system (Becton Dickinson) for the identification of mycobacterial complexes/species, employing chemical compounds as selective inhibitory agents or for testing biochemical activities. Thirteen tests are presented and discussed.-Authors' Abstract
Soini, H., Skurnik, M., Liippo, K., Tala, E. and Viljanen, M. K. Detection and identification of mycobacteria by amplification of a segment of the gene coding for the 32-kilodalton protein. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30(1992)2025-2028.
A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) assay for the rapid detection of mycobacterial DNA is described. Oligonucleotide primers, derived from the sequence of a gene coding for the 32-kDa antigen of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, amplified DNA from all 28 species of mycobacteria tested. All nonmycobacterial species tested were negative. An oligonucleotide probe hybridized to the PCR products of the strains belonging to the M. tuberculosis complex. This method could detect as little as 50 fg, as tested with purified M. tuberculosis DNA. By this amplification method, 127 sputum specimens were tested, with 7.9% of the specimens proving to be inhibitory in PCR. The sensitivity of detection by PCR compared with that by culture was 55.9%; when the inhibitory specimens were excluded, the sensitivity was 70.4%. The specificity of PCR combined with hybridization was 100%.- Authors' Abstract
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PREVENTION
Abe, M., Ozawa, T., Minagawa, F. and Yoshino, Y. Immunoepidemiological studies on subclinical infection in leprosy. I. Clinical and immunological findings in schoolchildren and adults in Okinawa. Jpn. J. Lepr. 59(1990)130-144.
For the purpose of understanding subclinical infection with Mycobacterium leprae among the inhabitants in an endemic area, 3547 schoolchildren and 1487 adults in several regions of Okinawa were surveyed by using clinical examinations and immunological tests, i.e., the fluorescent leprosy antibody absorption (FLA-ABS) test and the lepromin test using Dharmendra's antigen, during a period from 1978 to 1984. The enlargement of peripheral nerves, especially that of lateral or bilateral auricular and/or ulnar nerves, without loss of sensation was found in 8.4% of the schoolchildren and in 9% of the adults. A frequency of these signs and symptoms was significantly higher in male than in female and tended to increase with age. The percentage of positive reactions in FLA-ABS tests for schoolchildren and adults was 21.8 and 22.5, respectively, the values suggesting a minimum frequency of subclinical infection with M. leprae among these inhabitants. The percentage of positive FLA-ABS tests was significantly higher in those with neural signs and symptoms than in those without. Such a correlation was not found in the lepromin test. Ill-defined depigmentation of the skin without loss of sensation was found in a small percentage of both schoolchildren and adults. However, these signs and symptoms did not correlate with the FLA-ABS test nor with the lepromin test. A history of tuberculin test and I3CG vaccination in the schoolchildren seemed to influence the lepromin reactivity. Among 770 schoolchildren tested with both FLA-AI3S and lepromin, 70 (9.1%) were FLA-AI3S positive but lepromin nonpositive responders. Neural signs and symptoms were found in 31 of these children. -Authors' Abstract
Dayal, R. Early detection of leprosy in children. J. Trop. Pediatr. 37(1991)310-312.
Healthy children contacts of leprosy patients [in Agra, India] had their humoral and cell-mediated immunological status assessed using the fluorescent leprosy antibody absorption technique (FLA-ABS) and the lepromin test, respectively. Subsequently, they were followed up for 2.5 years to study the development of overt disease.
Two hundred children were studied and classified into 4 groups: Group I comprised of children who were FLA-ABS positive and lepromin positive; Group II = FLA-ABS positive and lepromin negative; Group III = FLA-ABS negative and lepromin positive; Group IV = FLA-ABS negative and lepromin negative. The good cell-mediated immune (CMI) response in the 107 children in Group I prevented them from developing the disease although they had been infected. Out of the 37 children in Group II, 15 developed the disease. There were no children in Group III. None of the 56 children in Group IV developed the disease, possibly because they had not been significantly infected. All these findings were statistically significant (p < 0.01). This study highlights the protective role of cell-mediated immunity in leprosy. It also suggests the need to carry out surveillance surveys in the endemic population to identify and follow up those at risk.-Author's Summary
Kotecha, P. and Harpham, T. Can leprosy be eradicated from India? Health Policy Plan. 6(1991)82-85.
Writing from the Medical College in Baroda, India, and the Health Policy Unit at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, the authors draw attention to the stated commitment of the government of India to eradicate leprosy by the year 2000 and to the strong political will behind the leprosy program in India, which is by far the largest in the world (4 million estimated cases in 1981). They review the characteristics of the National Leprosy Eradication Programme (NLEP) and describe the problems which have been encountered, drawing attention to the large number of vacant posts in the program, the inherent difficulties of population surveys, and the logistic and administrative constraints with regard to drug distribution and compliance. The main emphasis of the paper centers on the conclusion that the decision of the Indian government to aim for eradication is unrealistic: "The aim to eradicate leprosy from India was political-no technical expert would have thought eradication by the year 2000 was feasible."-From A. C. McDougall (Trop. Dis. Bull.)
Leprosy situation in selected countries: abstracts from the 64th General Meeting of the Japanese Leprosy Association held in March 1991. Jpn. J. Lepr. 60(1991)54-59.
Leprosy in Pakistan (population 110 million) is a focal problem with a total number of registered cases at the end of 1989 of 34,886; 12,284 patients were under treatment. The total number of cases inclusive of refugees is estimated at over 40,000; 1225 new cases were registered in 1988-1989. Multiple drug therapy (MDT) is used.
In The Philippines, segregation of active cases was compulsory until 1964. The prevalence rate is 0.68/1000 population overall, but in 10 endemic provinces ranges from 1.08 to 3.89/1000. There were 38,837 registered active cases in 1987 (ratio of multibacillary to paucibacillary cases 55:45). Of newly detected cases, 14.5% were in children aged < 4 years. MDT is in operation.
Jiangsu province (population 65 million) is situated on the east coast of China. Over 1400 staff are employed in the province's leprosy clinics. By the end of 1989, 1200 active cases were registered, a prevalence rate of 0.0185/1000 (compared with 0.63/ 1000 in 1973). The number of cases detected annually averaged 234 in 1984 to 1988 but only 129 were detected in 1989. MDT is used whenever appropriate. Basic elimination of leprosy from the province is hoped to be achieved by 1993.
The estimated prevalence of leprosy in Thailand in 1953 was 5/1000 population (104,000 patients). Dapsone monotherapy, used until 1983, caused a reduction in prevalence to 1.23/1000 in 1971 and 0.9/1000 in 1983. Almost all (92%) of cases have been given MDT between 1984 and 1990. In 1989, the number of registered cases was 17,294 (0.31/1000) and or the newly registered cases was 1594. The leprosy control program, particularly MDT, is considered to have been successful.
There were an estimated 4 million leprosy cases in India in 1987, with 45% of the 435 districts having a prevalence rate > 5/1000 in 1986. Throughout the country the annual case detection rate has been 0.4 to 0.5 million new cases for each of the 8 years up to 1991. In 1991, 112 districts were covered by a modified MDT program (2.1 million cases); by 1992, 90% of cases were to be covered by MDT and by 1995 all districts were planned to be in the scheme. - C. A. Brown (Trop. Dis. Bull.)
Li, B., et al. [Analysis of 545 active cases ofleprosy in Shandong.] China Lepr. J. 8(1992)14-15. (in Chinese)
By the end of 1989, there remain only 668 active cases of leprosy in Shandong province, of which 545 having complete records were analyzed. Among them 376 cases (69%) are incipient with a mean age of 39.8 years at onset, and the ratios of MB to PB and male to female are 3.32 to 1 and 2.48 to 1, respectively. When diagnosed, the duration of the disease was less than 1 year in 29.1% of MB and in 43.7% of PB. MDT was very effective as BI decreased by 0.56 a year on the average. The other 169 cases are relapsed, accounting for 31% of analyzed cases. Among them the ratio of male to female is 7 to 1, while those who have relapsed over 10 years after cured amount to 65.1% of relapses. -Authors' English Abstract
Mastro, T. D., Redd, S. C. and Breiman, R. F. Imported leprosy in the United States, 1987 through 1988-an epidemic without secondary transmission. Am. J. Pub. Health 82(1992)1127-1130.
Leprosy remains a major health problem in many regions of the world. In the United States, although leprosy continues to be reported, approximately 90% of cases are imported (i.e., occur among immigrants and refugees). An increase in imported cases began in 1978. This study was conducted to analyze this trend and to characterize the contributing cases. Centers for Disease Control leprosy surveillance data from 1971 through 1988 were analyzed. The number of imported cases reported annually was relatively constant from 1971 through 1977 (mean =11 9 per year), increased to 307 in 1985, and then decreased to 102 in 1988. Of the 957 excess cases reported from 1978 through 1988, 73.4% were among persons from Southeast Asia, including 51.3% from Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos (Indochina). There was no coincident increase in indigenous cases of leprosy; the mean annual number of such cases was 17.7 (range = 10 to 29). Leprosy remains endemic in Texas, Hawaii, Louisiana, and possibly California. An epidemic of imported leprosy began in the United States in 1978, peaked in 1985, and ended by 1988. This increase was primarily due to cases among refugees from Indochina and was limited by a decrease in the influx of Indochinese refugees in the mid 1980s. There is no evidence that these cases resulted in transmission in the United States. -Authors' Abstract
Tang, Q.-G., et al. [A comparison between agglutination test with gelatin particles sensitized by NT-P-BSA and ELISA.] China Lepr. J. 7(1991)218-220. (in Chinese)
Agglutination tests with gelatin particles sensitized by NT-P-BSA and ELISA with NT-O-BSA as coating antigen were made in 1334 specimens of serum. The results showed the coincidence of both in 1309 specimens, including 120 positive and 1189 negative in both the tests, with a coincidence rate of 98.1%. The positive rate in both tests at the same time is 1.7% in vocational contacts with leprosy, 2.16% in social contacts, and 2% in healthy population. The patients with tuberculosis all showed negative in both. There was no significant difference among them. But the positivity in the household contacts with leprosy was 8%, four times that in the healthy population. The positive household contacts are being followed. The positivity in the GPAT was mostly seen in BL-LL leprosy patients, indicating that the GPAT has higher specificity to the antibody against PGI and seems to be useful in the detection of early cases of leprosy and the population at risk of contracting leprosy. -Authors' English Abstract
REHABILITATION
Chen, X.-S., et al. [A sociomedical investigation on leprosy disability -a survey of marriage in patients with leprosv disability.] China Lepr. J. 7(1991)205-210. (in Chinese)
A survey of the marital status of 2500 registered leprosy patients in the cities of Yangzhou and Dongtai, Jiang-su Province, showed that the unmarried, divorced and remarriage rates were 28%, 6.0% and 12.5%, respectively, and that the unmarried rate (28.7%) and divorced rate (6.1%) in patients with disability were significantly higher than those in patients without disability (16.8% and 3.8%). Both the rates in disabled patients with a disability index over two were even higher than those in undisabled ones, with the relative risk (RR) being over 4.0 and 3.0, respectively. Both the RRs of nonmarriage and divorce in patients with deformity of their faces were over 2.5. The mean age of marriage in patients who got married after disability was 4.3 years later than that in patients who got married before disability. The mean marriage duration in divorced patients was 4.6 years. The authors conclude that the marriage of patients with deformity and disability was one of important problems of leprosy to society and its reasonable solution would be advantageous to the physical, psychological and social rehabilitation for them and to the ultimate achievement of the eradication of leprosy. Some comprehensive measures relevant to the solution of this problem have been recommended. -Authors' English Abstract
OTHER MYCOBACTERIAL DISEASES AND RELATED ENTITIES
Altamirano, M., Kelly, M. T., Wong, A., Bessuille, E. T., Black, W. A. and Smith, J. A. Characterization of a DNA probe for detection of Mycobacterium-tuberculosis complex in clinical samples by polymerase chain reaction. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30(1992)2173-2176.
We cloned and sequenced a DNA fragment from Mycobacterium tuberculosis for use in the identification of members of the M. tuberculosis complex. The DNA probe for culture confirmation had a sensitivity and a specificity of 100%. By using primers developed from this probe, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) detected 20 mycobacteria by cthidium bromide staining. This PCR system demonstrated 98% sensitivity and 100% specificity for detection of the M. tuberculosis complex in 200 sputum specimens.-Authors' Abstract
Barrios, C, Lussow, A. R., Van Embden, J., Vanderzee, R., Rappuoli, R., Costantino, P., Louis, J. A., Lambert, P. H. and Delgiudice, G. Mycobacterial heat-shock proteins as carrier molecules. 2. The use of the 70-kDa mycobacterial heat-shock protein as carrier for conjugated vaccines can circumvent the need for adjuvants and bacillus-Calmette-Guérin priming. Eur. J. Immunol. 22(1992)1365-1372.
In a recent work, we have shown that mycobacterial heat-shock proteins (hsp) of 65-kDa (Gro£L-type) and 70-kDa (DnaKtype) acted as carrier molecules in mice, previously primed with Mycobacterium tuberculosis var. bovis (bacillus Calmette-Gucrin, I3CG), for the induction of high and longlasting titers of IgG against the repetitive malaria synthetic peptide (NANP)40. Antipeptide antibodies were induced when the malaria peptide, conjugated to the mycobacterial hsp, was given in the absence of any adjuvants (Lussow, et al., Eur. J. Immunol. 1991, 87: 2960). In this report, we show that mice immunized with peptides or oligosaccharides conjugated to the 70kDa hsp produced high titers of IgG antibodies in the absence of any previous priming with BCG. The anti-peptide antibody response persisted for at least 1 year. This adjuvant-free carrier effect of the 70-kDa hsp was T-cell dependent, since no antipeptide nor anti-70-kDa IgG antibodies were induced in athymic nu/nu mice. Previous immunization of mice with the 65kDa or 70-kDa hsp did not have any negative effect on the induction of anti-peptide IgG antibodies after immunization with hsppeptide conjugates in the absence of adjuvants. Furthermore, preimmunization with the 65-kDa hsp could substitute for BCG in providing an effective priming for the induction ofanti-(NANP) antibodies. Finally, both the 65-kDa and 70-kDa hsp acted as carrier molecules for the induction of IgG antibodies to group C meningococcal oligosaccharides, in the absence of adjuvants. These findings strongly suggest that the use of hsp as carriers in conjugated constructs for the induction of anti-peptide and antioligosaccharide antibodies could be of value in the design of new vaccines for eventual use in humans.-Authors' Abstract
Batungwanayo, J., Taelman, H., Dhote, R., Bogaerts, J., Allen, S. and Vandeperre, P. Pulmonary tuberculosis in Kigali, Rwanda-impact of human immunodeficiency virus infection on clinical and radiographic presentation. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 146(1992)53-56.
The aim of the present study was to compare the clinical and radiographic presentation as well as the therapeutic outcome of pulmonary tuberculosis (PT) in adult patients with and without human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) infection in Kigali, Rwanda. Over a 17-month period, 59 consecutive patients with bacteriologically and/or histopathologically documented PT were enrolled. Of these, 48 (81%) patients were HIV seropositive. Among these, 35 fit the WHO clinical criteria for AIDS (WHOCCA) at the time of admission. Significant differences were found between the HIV-seropositive and HIV-scronegative groups of patients: fever (85% vs 36%; p < 0.001 ), tuberculin skin test ancrgy (69% vs 0%; p < 0.01), mediastinal and/or hilar adenopathies (31% vs 0%; p = 0.05), and pleural effusion (43% vs 9%; p < 0.05) were more frequently encountered in the HIV-seropositive group, and upper lobe infiltrates (55% vs 16%; p < 0.02) and cavitation (91% vs 39%; p < 0.003) were more often seen in the HIV-seronegative group. However, HIV-seropositive patients not meeting WHOCCA were less frequently anergic (0% vs 100%; p < 0.001) and feverish (53% vs 97%; p < 0.01) and more often had cavitation (69% vs 28%; p < 0.02) and less often mediastinal and/or hilar adenopathies (7% vs 40%; p < 0.004) compared with HIV-seropositive patients meeting WHOCCA. Under antituberculosis treatment, clearance of fever was slower in HIV-seropositive compared with HIV-seronegative patients, and among the HIVseropositive group it was slower in those fitting WHOCCA. Data collected from this study suggest that the clinical severity and the radiographic pattern of HIV-associated PT are strongly related to the degree of progression of HIV infection. Although slower in advanced HIV infection, a favorable response to antituberculosis treatment was observed in all these groups of patients.- Authors' Abstract
Besra, G. S., McNeil, M. R. and Brennan, P. J. Characterization of the specific antigenicity of Mycobacterium fortuitum. Biochemistry 31(1992)6504-6509.
Mycobacterium fortuitum, biovar. fortuitum, the cause of serious skin and soft-tissue infections, can be differentiated from M. fortuitum, biovar. peregrinum, and other rapidly growing opportunistic mycobacteria by the presence of a unique antigenic glycolipid. The glycolipid is among the simplest of the acyltrehalose-containing lipooligosaccharide class. The application of H-l and C-13 NMR, methylation analysis, FAB/ MS, and other procedures demonstrated the structure, beta-D-Glcp-(l → 6)-2-0-acyl-alpha-D-Glcp-l(l ↔ l)-3,4,6-tri-0-acyl-alpha-D-Glcp. Thus, practically all environmental mycobacteria, many of them opportunistic pathogens, can be differentiated serologically and chemically on the basis of unique sugar arrangements within a few classes of glycolipids. The simplicity of the structure in M. fortuituin fortuitum combined with the distinct roughness of the parent strain raises the intriguing possibility that it is a spontaneous rough variant of the other mycobacteria with more elaborate glycolipids. -Authors' Abstract
Bocart, D., Lecossier, D., Delassence, A., Valeyre, D., Battesti, J. P. and Hance, A. J. A search for mycobacterial DNA in granulomatous tissues from patients with sarcoidosis using the polymerase chain reaction. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 145(1992)1142-1148.
We have used the polymerase chain reaction as a tool to detect the presence of mycobacterial DNA from organisms of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex and other species of mycobacteria in samples from patients with sarcoidosis. Using systems based on the amplification of a fragment of the gene coding for the 65-kDa mycobacterial antigen, which were demonstrated to detect approximately 20 mycobacterial genomes/µg total DNA, DNA from M. tuberculosis was reproducibly identified in DNA extracted from granulomatous tissues from two patients with sarcoidosis, but could not be detected in DNA extracted from tissue biopsies (N = 16) or cells recovered by lavage (N = 6) from most sarcoid patients or from control subjects (N = 22). Using a system based on the amplification of a fragment of the IS6110 insertion element, which could reliably detect two genomes of mycobacterial DNA//xg total DNA, no additional positive results were observed. In an effort to identify another species of Mycobacterium present in granulomatous tissues from sarcoid patients but not control tissues, a fragment of the 65-kD mycobacterial antigen was amplified and then reamplified using "nested" primers recognizing sequences that are highly conserved among mycobacteria and closely related species, and the amplified DNA products were cloned and sequenced. Amplified DNA was observed in a minority of samples from patients and control subjects (32/84 and 34/77 attempts, respectively, p > 0.2), resulting from amplification of DNA from at least 17 different organisms. Most sequences were identified in both patients and control subjects or only in control subjects; the seven sequences that were identified only in samples from sarcoid patients were identified on only one, or at most, two occasions. We conclude that DNA from M. tuberculosis can be identified in a minority of patients with sarcoidosis, and it may play a pathogenetic role in such cases. If, however, this or another single mycobacterial species plays a pathogenic role in most patients with sarcoidosis, it must be present in established lesions at levels below the threshold of detection reached in these studies (< 15 organisms/106 human cells).-Authors' Abstract
Bottger, E. G, Teske, A., Kirschner, P., Bost, S., Chang, H. R., Beer, V. and Hirschel, B. Disseminated "Mycobacterium genavense" infection in patients with AIDS. Lancet 1(1992)76-80.
We describe 18 patients with advanced HIV infection, most of whom had a chronic illness characterized by fever, diarrhea, and massive loss of weight. Biopsy and necropsy samples revealed abundant acid-fast microorganisms in intestines, liver, spleen, lymph nodes, and many other tissues, which did not grow on solid media, although limited growth was observed in liquid blood cultures. Using primers complementary to bacterial 16S rRNA, we amplified DNA sequences from tissue and leukocyte extracts and from blood-culture bottles. The sequences obtained were unique and suggest that the microorganism is a new member of the genus Mycobacterium, for which we propose the name "Mycobacterium genavense." Disseminated infection with "M. genavense" should be considered in the differential diagnosis of HIV-infected patients with extreme immunosuppression, wasting, and fever.-Authors' Abstract
Cormican, M. G., Barry, T., Gannon, F. and Flynn, J. Use of polymerase chain reaction for early identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in positive cultures. J. Clin. Pathol. 45(1992)601-604.
Aims: To develop a readily applicable polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-based technique which would permit the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex isolates from BACTEC phials at an earlier stage than currently available methods.
Methods: Mycobacterial cells cultured in BACTEC 12B medium were harvested by centrifugation. The cells were lysed by heating in distilled water. Oligonucleotide primers based on the sequence of the gene coding for the immunogenic protein MPB64 were then used to amplify a 240 base pair fragment of DNA directly from the crude cell lysate. The PCR product was visualized under ultraviolet light following electrophoresis of an aliquot in an agarose gel .containing cthidium bromide. The sensitivity of the PCR was adjusted so that about 600 cfu of M. tuberculosis gave a positive result. The lowest growth index at which this method of identification might be applied to BACTEC phials was determined, and a number of routine cultures giving a positive growth index examined.
Results: M. tuberculosis was positively identified at the lowest growth index, as determined by the BACTEC system. Of 45 routine cultures examined, with growth index ranging from 6 to 999, the 15 confirmed by conventional means to contain M. tuberculosis were correctly identified from 1 ml of culture medium.
Conclusions: The method described can be used to identify M. tuberculosis isolates cultured in the BACTEC system at the earliest detectable rise in growth index. It may therefore allow cultured mycobacteria to be identified at an earlier stage than conventional methods or the commercially available DNA probes adapted for use with the BACTEC system. -Authors' Abstract
Cynamon, M. H. and Klemens, S. P. Activity of azithromycin against Mycobacterium avium infection in beige mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36(1992)1611-1613.
The comparative activities of azithromycin and clarithromycin and the activities of azithromycin alone and in combination with other antimycobacterial agents were evaluated in the beige mouse model of disseminated Mycobacterium avium complex infection. Azithromycin was similar in activity to clarithromycin. Azithromycin plus clofazimine plus ethambutol reduced the number of splenic organisms more than azithromycin alone, while the combination was less active than azithromycin alone for bacteria in lungs. Rifabutin had activity similar to that of azithromycin for organisms in spleens and lungs. Rifabutin plus azithromycin was more active than either agent alone for organisms in spleens, but the combination's activity was not significantly different from that of rifabutin for organisms in lungs. The activity of azithromycin against several M. avium complex isolates was evaluated. The reduction of viable cell counts in spleens ranged from 1.7 to 0.8 log units. For the three isolates studied, there was little correlation between the in vitro MIC and the in vivo activity.-Authors' Abstract
Daugelat, S., Guile, H., Schoel, B. and Kaufmann, S. H. E. Secreted antigens of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-characterization with lymphocytes-T from patients and contacts after two-dimensional separation. J. Infect. Dis. 166(1992)186-190.
Little is known about T-cell antigens involved in immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Most model systems use in vitro culture of human T lymphocytes with bacterial lysates or secreted proteins as antigens. In this study, proteins from 3-weekold M. tuberculosis culture filtrates were separated by two-dimensional PAGE and subsequently transferred into soluble phase. The resulting 480 fractions were screened with T lymphocytes from tuberculosis patients and healthy contacts. T cells from all 9 patients and from 8 of 10 tuberculin-positive contacts preferentially responded to a cluster of acidic proteins (pi 4-5) with molecular masses of30-100 kDa, although they also recognized a number of other fractions. In contrast, of 7 tuberculin-negative contacts, 4 were not and 3 were only weakly stimulated by this cluster region. Therefore, this distinct cluster of secreted proteins seems to comprise dominant T-cell antigens of M. tuberculosis.- Authors' Abstract
Delalla, R., Maserati, R., Scarpellini, P., Marone, P., Nicolin, R., Caccamo, F. and Rigoli, R. Clarithromycin-ciprofloxacin-amikacin for therapy of Mycobacterium avium-Mycobacterium intracellular bacteremia in patients with AIDS. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36(1992)1567-1569.
A combination of clarithromycin, ciprofloxacin, and amikacin for the treatment of Mycobacterium avium -M. intracelulare bacteremia was evaluated in 12 AIDS patients. Mycobacteremia cleared in all patients by 2 to 8 weeks of treatment, and symptoms resolved. Four patients died; all had negative blood cultures until death, and disseminated M. avium-M. intracellulare complex infection was not considered the primary cause of death. -Authors' Abstract
Elsaghier, A., Nolan, A., Allen, B. and Ivanyi, J. Distinctive Western blot antibody patterns induced by infection of mice with individual strains of the Mycobacterium avium complex. Immunology 76(1992)355-361.
Systemic infection of mice with organisms of the Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) induced antibody responses, characteristic for each of the three tested individual strains. The influence of host genetic factors was reflected up to 3 months after infection by the finding of generally oligobanded and multibanded Western blot patterns in C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice, respectively. Nevertheless, more bands developed at 6 months in C57BL/6 mice. The response to three antigens of 18,000, 38,000 and 24,000 MW was analyzed in greater detail. Antibodies to a protease-resistant 18,000 MW band produced only by BALB/c mice were either strain specific, following infection with M. avium, strain Maa-B2, or crossreactive within MAC, following infection with M. avium strain Maa-A6 and M. paratuberculosis, strain Map-203. Another protease-resistant antigen of 38,000 MW was immunogenic only in Maa-B2 infected mice. This constituent was found to be related to the protease-sensitive antigen of corresponding molecular weight from M. tuberculosis. Two 24,000 MW proteins of M. paratuberculosis were separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis: antibodies to the anodic band were induced by Map-203 infection, while the cathodic band was revealed by heteroclitic antibodies from Maa-B2-infected mice. The latter antigen is apparently expressed during in vivo replication, but not during in vitro culture of Maa-B2 bacteria. We generally conclude that the selective antibody patterns after live infection could be attributed to differences in the release of native antigens within mycobacterial lesions. In view of a high degree of species specificity, some of the immunogenic constituents identified may also be useful for sérodiagnostic application.-Authors' Abstract
Epstein, M. L., Windebank, K. P., Burt, A. D., Thomas, L. and Cant, A. J. CD30 expression by peripheral blood monocytes and hepatic macrophages in a child with miliary tuberculosis. J. Clin. Pathol. 45(1992)638-639.
The peripheral blood of a 3-month-old boy with disseminated tuberculosis showed CD30 positive monocytes on flow cytometric analysis. His liver contained CD30 positive-staining macrophages and giant cells. CD30 is an activation antigen which has not been previously found on peripheral blood monocytes.-Authors' Abstract
Fattorini, L., Hu, C. Q., Jin, S. H., Santoro, C, Tsang, A. Y., Mascellino, M. T., Mandler, F. and Orefici, G. Activity of antimicrobial agents against Mycobacterium avium intracellulare complex (MAC) strains isolated in Italy from AIDS patients. Zentralbl. Bakteriol. [A] 276(1992)12-520.
Twenty-five strains of Mycobacterium avium-intracellulare (MAC) isolated from acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) patients in three medical centers in Italy have been studied. Scrotyping performed on 18 strains showed various serovars within either M. avium or M. intracellular serotypes and with serovars 1 and 21 being the most prevalent (four strains for each serovar). Among 14 drugs used for testing the antibiotic sensitivity, rifapentine, rifabutin and clofazimine showed to have the best in vitro activity. In an ex vivo model of infection using peritoneal resting macrophages from the C57BL/6 mouse, the intracellular viability of a strain of M. avium (strain 489, serovar 3) was reduced by clofazimine, amikacin, ciprofloxacin, rifabutin and clarithromycin (99%, 98%, 93%, 89% and 69%, respectively), thus indicating for clofazimine a good correlation between in vitro and ex vivo activity.-Authors' Abstract
Fattorini, L., Orefici, G., Jin, S. H.,,Scardaci, G., Amicosante, G., Franceschini, N. and Chopra, I. Resistance to beta-lactams in Mycobacterium fortuitum. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36(1992)1068-1072.
It is widely assumed that the high level of intrinsic resistance to beta-lactam antibiotics exhibited by mycobacteria results from the combination of factors including permeability to the drugs, beta-lactamase production, and affinity for penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). We conducted an evaluation of the second and third factors by isolating nitrosoguanidine-induced mutants from the beta-lactamase-producing strain Mycobacterium fortuitum ATCC 19542 that displayed either elevated or reduced resistance to various beta-lactam antibiotics. The mutants studied included Dl (a beta-lactamase producer with high penicillin resistance), gamma-27 (a low-level beta-lactamase producer with low penicillin resistance), and D316 (a high-level beta-lactamase producer with high penicillin resistance). In all strains examined, four major PBPs, named 1, 2a, 2b, and 3, with apparent molecular weights of 102,000, 90,000, 87,000, and 50,000, respectively, were found. The MICs of various beta-lactams toward ATCC 19542 and its mutants were considered in the context of beta-lactamase production, the quantity of PBPs synthesized, and their affinities for beta-lactam antibiotics. The data obtained show that beta-lactamase production is likely to be an important factor in the expression of resistance by clinical isolates and that PBP alterations can contribute to resistance at least in laboratory-derived mutants. -Authors' Abstract
Figueiredo, J. F. C. and Machado, A. A. Reduced anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis antibody response in tuberculosis patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 25(1992)611-618.
When the sera of patients with tuberculosis were tested for anti-Mycobacterium tuberculosis IgG using an indirect ELISA, the test was positive for 94.1% of the samples from patients not having AIDS (N = 51) but for only 37.5% of the samples from patients with AIDS (N = 16). False-positive results were obtained for 7.3% of patients not infected with HIV (N = 96) and for 4.7% of patients infected with HIV (N = 64). In most serum samples obtained from patients with tuberculosis and AIDS after the beginning of specific treatment, there was a reduction of the ELISA absorbance at 490 nm with time. These results indicate that serological tests for the detection of anti-M tuberculosis IgG in patients with AIDS are of limited value for the diagnosis of tuberculosis, most likely as a consequence of the underlying immune defect of the patients. - Authors' Abstract
Fischer, H. P., Sharrock, C. E. M. and Panayi, G. S. High frequency of cord blood lymphocytes against mycobacterial 65kDa heat-shock protein. Eur. J. Immunol. 22(1992)1667-1669.
A high frequency of nonadherent mononuclear cells in human cord blood proliferates in response to mycobacterial 65-kDa heat-shock protein. The frequency range in cord blood is not different from that in peripheral blood of bacillus Calmette-Guérinvaceinated adults. In comparison we found 10 to 100 times lower frequencies to purified protein derivative in nonadherent cord blood mononuclear cells than in adult peripheral blood mononuclear cells. These findings may provide experimental support for Cohen's theory of the immunological homonculus. -Authors' Abstract
Gevaudan, M. J., Bollet, C, Mallet, M. N., Delamballerie, X., Sambuc, R. and Demicco, P. Extracellular and intracellular activities of Sparfloxacin against Mycobacterium avium complex and Mycobacterium xenopi. Pathol. Biol. 40(1992)443-449.
Activity of the new fluoroquinolone Sparfloxacin against 30 strains of Mycobacterium avium complex and 25 strains of M. xenopi was tested in vitro. Sparfloxacin was used alone (determination of MICs and MBCs) and in combination with cthambutol and rifabutin. Synergy studies with determination of the FIC and FBC indices showed that the sparfloxacin-ethambutol combination was synergistic against 10 M. avium complex strains and 12 M. xenopi strains. With the three-drug combination (sparfloxacin-ethambutol-rifabutin), synergy was found against 12 M. avium and 14 M. xenopi strains. Studies of intracellular bacteria showed that the decrease in viable bacteria with the three-drug combination was 1 log for M. avium and 2 logs for M. xenopi. -Authors' English Abstract
Gosselin, D., Turcotte, R. and Lemieux, S. Cyclophosphamide treatment antagonizes the in vitro development of Mycobacterium lepraemurium-induced suppressor cell precursors. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 89(1992)185-191.
The in vitro-inducible maturation of splenic suppressor cell precursors detected during the early phase of Mycobacterium lepraemurium infection can be abrogated when a high dose of cyclophosphamide (Cy) is inoculated to infected mice 2 days before assay. The drug does not act directly on adherent suppressor cell precursors, but rather inhibits their activation by a nonadherent cell subset whose phenotype has not yet been elucidated. It was established by flow cytometry analyses that despite a marked increase in the total number of splenic nonadherent cells following M. lepraemurium infection, the effect of Cy on Ia + , Thy-1 +, CD4+ and CD8+ cells in infected mice was comparable to that observed in normal controls. It was not possible to determine the duration of the inhibiting effect of Cy on nonadherent regulatory cells because the drug was itself inducing suppressor cells from 7 days after inoculation. By the time spleencell suspensions were totally free of Cy-induced suppressor cells, infection-dependent suppressor-cell precursors were once again detected, indicating that Cy treatment did not prevent their in vivo accumulation. Therefore, even though M. lepraemurium-induced, adherent suppressor-cell precursors are themselves fully resistant to Cy, their development is transiently abrogated by the drug, most probably through the impairment of a nonadherent cell subset regulating their maturation. -Authors' Abstract
Heifets, L and Lindholm-Levy, P. Pyrazinamide sterilizing activity in vitro against scmidormant Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacterial populations. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 145(1992)1223-1225.
Previously, we reported that pyrazinamide has very poor bactericidal activity against M. tuberculosis growing in broth at pH 5.6. In the present study, cultivation at pH 4.8 to 5.0 in 7H12 broth prevented an increase in the number of viable bacteria, but the cultures remained metabolically active. The presence of 50-µg/ml pyrazinamide in scmidormant cultures led to a sharp decline in the number of viable bacteria, by more than 1000-fold. This unfavorable environment probably made the bacilli especially vulnerable to pyrazinamide, whose mode of action remains unclear. To distinguish this effect of pyrazinamide on the scmidormant bacteria from its mostly bacteriostatic activity against actively multiplying bacteria, we suggest interpreting the in vitro effect as "sterilizing."-Authors' Abstract
Ito, M., Kojiro, N., Ikeda, T., Ito, T., Fuñada, J. and Kokubu, T. Increased proportions of peripheral blood gamma/delta T cells in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis. Chest 102(1992)195-197.
There is a small population of peripheral T cells bearing the gamma-delta T-cell receptor which may be involved in the defense against invading microorganisms and tumor cells. The present study was designed to evaluate the levels of gamma-delta T cells in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis, bacterial pneumonia, chronic lower respiratory tract infection, lung cancer, and normal control subjects with or without an old tuberculous lesion. The results showed that only patients with tuberculosis had significantly increased proportions of peripheral blood gamma-delta T cells. This study suggests that the increased proportions of gamma-delta T cells in tuberculosis could be related to T-cell activation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, although it remains to be investigated which components of mycobacteria are the major ligands for gammadelta T cells.-Authors' Abstract
Jeevan, A.,Evans, R., Brown, E. L. and Kripke, M. L. Effect of local ultraviolet irradiation on infections of mice with Candida albicans, Mycobacterium bovis BCG, and Schistosoma mansoni. J. Invest. Dermatol. 99(1992)59-64.
In this study, we investigated whether mice given ultraviolet (UV)-B (280-320 nm) radiation in doses sufficient to alter cutaneous immune cells and impair the induction of contact hypersensitivity would also have impaired resistance to infectious agents administered at the site of UV irradiation. C3H mice were exposed to 400 J/m2 UVR from FS40 sunlamps on four consecutive days. Immediately after the last UV treatment, groups of mice were injected subcutaneously with Candida albicans, injected intradermally (ID) with Mycobacterium bovis bacillus Calmette-Guerin (BCG), or infected percutaneously with Schistosoma mansoni in UV-irradiated skin. The induction of the delayed hypersensitivity response to C. albicans and BCG, as assessed by foot pad swelling, was unaffected by UV irradiation. However, the number of viable mycobacteria recovered from the lymphoid organs of BCG-infected mice was increased significantly in the UV-irradiated animals for a period of more than 2 months. Lowdose UV irradiation of the skin at the site of infection did not influence the number of S. mansoni parasites recoverable from the internal organs of mice that had been infected with cercariae percutaneously 6 weeks earlier. We conclude that the ability of UV radiation to impair the development of cell-mediated immunity to antigens introduced in a UV-irradiated site is not universal and depends on the particular antigen administered. We hypothesize that the involvement of epidermal Langerhans' cells as the primary antigen-presenting cells in the induction of cell-mediated immunity may be the critical factor in determining whether a particular immune response will be affected by local UV irradiation.-Authors' Abstract
Laszlo, A., Baer, H. H., Goren, M. B., Handzel, V., Barrera, L. and de Kantor, I. N. Evaluation of synthetic pseudo cordfactor-like glycolipids for the serodiagnosis of tuberculosis. Res. Microbiol. 143(1992)217-223.
A number of glycolipids were evaluated in an ELISA for their sérodiagnostic usefulness in tuberculosis. One-hundred-twelve (112) sera belonging to bacteriologically confirmed TB patients, patients with pathologies other than tuberculosis, and healthy individuals were examined against several synthetic "mirror" pseudo cord factors (analogs of trehalose-6, 6'-dimycolate or TDM) using natural cord factor and another recently described natural glycolipid (SL-IV) of Mycobacterium tuberculosis as control antigens. Analysis of the results shows that all synthetic "mirror" pseudo cord factors, except one with a short 8-carbon chain, were better recognized by the sera of tuberculosis patients than natural cord factor, with sensitivity and specificity values in the ELISA similar to those reported for M. tuberculosis species-specific SL-IV. Of all antigens tested in this study, BDA.TDA, a bis( A/.N-dioctadecylamide) of "trehalose dicarboxylic acid," [(a-D-glucopyranosyluronic acid) (a-D-glucopyranosiduranic acid)], showed the highest sérodiagnostic discriminating power (93% sensitivity and specificity). We postulate that either these artificial molecules are crossreactants of similarly structured native glycolipids of M. tuberculosis or that they bear closer resemblance to actual phagosome-lysosome-modified antigens than to native mycobacterial ones.-Authors' Summary
Laszlo, A., Papa, F. and David, H. L. Thinlayer chromatography systems for the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis BCG, M. kansasii, M. gastri, and M. marinum. Res. Microbiol. 143(1992)519-524.
Knowledge of mycobacterial glycolipid antigens and the study of their specificity have resulted in their utilization as species markers. We describe a thin-layer chromatography method which could serve as a useful adjunct for the identification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. bovis BCG, M. kansasii, M. gastri and M. marinum.- Authors' Abstract
Lemassu, A., Levy-Frebault, V. V., Laneelle, M. A. and Daflfe, M. Lack of correlation between colony morphology and lipooligosaccharide content in Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. J. Gen. Microbiol. 138(1992)1535-1541.
Rough and smooth colony variants of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex were compared with respect to their composition in trehalose-containing glycolipid antigens in view of the results of a recent investigation suggesting that the chemical basis of rough and smooth colony morphology in mycobacteria may reside in the occurrence of lipooligosaccharides. A careful chemical characterization of the individual glycolipids of the selected strains allowed the identification of the major glycolipids. The comparative study of the glycolipid content of the smooth Canetti strain, its spontaneous rough variant, and 16 additional strains of M. tuberculosis, M. bovis and M. africanum showed that the presence of lipooligosaccharides was not related to the morphology of the colonies.-Authors' Abstract
Nair, J., Rouse, D. A. and Morris, S. L. Nucleotide sequence analysis and serologic characterization of the Mycobacterium intracellularehomologuc of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 19-kDa antigen. Mol. Microbiol. 6(1992)1431-1439.
Disseminated Mycobacterium avium/ Mycobacterium intracellulare complex (MAC) disease is a frequent complication in patients with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). In this report, we present the nucleotide sequence of the M. intracellulare MI22 gene. Computer sequence comparisons reveal that the MI22 gene, which encodes a serologically active protein, has 78% DNA sequence identity and 77% protein sequence identity with the seroreactive 19 kDa M. tuberculosis lipoprotein antigen. Southern blot hybridizations indicate that an MI22 gene probe binds similar-sized restriction fragments in M. tuberculosis and M. intracellulare genomic DNA. In addition, immunoblot analyses demonstrate that MI22 is recognized by sera from tuberculosis patients. These data further support the existence of 19 kDa MAC and M. tuberculosis protein homologs. Phase partitioning experiments and the presence of a consensus lipid modification site in the deduced MI22 protein sequence strongly suggest that MI22 is also a lipoprotein. Comparative analyses of these mycobacterial antigenic homologs may provide the basis for the design of species-specific diagnostic reagents. -Authors' Abstract
Neway, T., Boulouis, H. J., Thibault, D. and Pilet, C. [Activities of polar glycopeptidolipids from Mycobacterium chelonae in the reversal of a chemically induced leucopenia.] C. R. Acad. Sei. [III] 315(1992)13-19. (in French)
Intraperitoneal administration of polar glycopeptidolipids extracted from Mycobacterium chelonae (GPLp-Mc) has led to reversal of doxorubicin-induced leukopenia in a manner comparable to that effected by GM-CSF administered in a dose of 100 IU (2.5-µg/kg). The action and the toxicity of this product are being studied. Results obtained on the mouse indicate that it would be worthwhile to undertake tests in man aimed at studying the effect of GPLp-Mc on chemotherapy- and radiotherapy-induced leukopenias, once toxicological studies have been carried out. -Authors' English Abstract
Nightingale, S. D., Byrd, L. T., Southern, P. M., Jockusch, J. D., Cal, S. X. and Wynne, B. A. Incidence of Mycobacterium avium intracellulare complex bacteremia in human immunodeficiency virus positive patients. J. Infect. Dis. 165(1992)1082-1085.
The product-limit incidence of Mycobacterium avium intracellulare complex (MAC) bacteremia in 1006 human immunodeficiency virus (HlV)-positive patients followed at one institution over a 3-year period from the day of AIDS diagnosis with monthly lysis-centrifugation blood cultures was 21% ± 2% SE at 1 year and 43% ± 3% at 2 years. The product-limit incidence of MAC bacteremia at 1 year after the patients' first CD4 cell count was related to both the CD4 cell count and to whether they had an AIDS diagnosis (both p < 0.0001) but not to age, sex, or race. This incidence was 39% ± 6% for CD4 cell counts of < 107mm3, 30% ± 5% for 10-19/mm3 20% ± 3% for 60-99/mm3 and 3% ± 1% for 100-199/mm3. MAC may eventually infect most if not all HIV-positive patients who do not die from another HIV-related event. -Authors' Abstract
Paul, J., Baigrie, C. and Parums, D. V. Fatal case of disseminated infection with the turtle bacillus Mycobacterium chelonae. J. Clin. Pathol. 45(1992)528-530.
An apparently immunocompetent 78 year-old woman presented with confusion, subcutaneous abscesses, and lesions of the nasopharynx. Gram-positive, acid-fast bacilli were isolated from her blood after 10 days' incubation. She was treated with trimethoprim-sulphamethoxazole for presumed disseminated nocardiasis but deteriorated and died. A post-mortem examination showed skin and pulmonary lesions and endomyocardial fibrous plaques. Organisms isolated from the skin and lung were indistinguishable from those cultured from the blood. The organism was subsequently identified as Mycobacterium chelonae. Primary pulmonary infection and disseminated disease are rarely caused by this organism and bacteremia is seldom documented. The clinical presentation and bacteriological and histological findings are difficult to differentiate from those of disseminated nocardiasis. Isolation of the organism may fail without prolonged incubation of initial cultures, and there is a danger of its being dismissed as medically unimportant. Diagnosis is further hampered because large pulmonary foci may be poorly revealed by conventional radiological examination of the chest. -Authors' Abstract
Pitulle, C, Dorsch, M., Kazda, J., Wolters, J. and Stackebrandt, E. Phylogeny of rapidly growing members of the genus Mycobacterium. Int. J. System. Bacterid. 42(1992)337-343.
The 16S rRNAs from nine rapidly growing Mycobacterium species were partially sequenced by using the didcoxynucleotideterminated, primer extension method with cDNA generated by reverse transcriptase. The sequences were aligned with 47 16S rRNA or DNA sequences that represented 30 previously described and 5 undescribed species of the genus Mycobacterium, and a dendrogram was constructed by using equally weighted distance values. Our results confirmed the phylogenctic separation of the rapidly and slowly growing mycobacteria and showed that the majority of the slowly growing members of the genus represent the most recently evolved organisms. The 24 strains which represented 21 rapidly growing species constituted several sublines, which were defined by the following taxa: (i) Mycobacterium neoaurum and M. diernhoferi, (ii) M. gadium, (iii) the M. chubuense cluster, (iv) the M. fortuitum cluster, (v) M. kommossense, (vi) M. sphagni, (vii) M. fallax and M. chitae, (viii) M. aurum and M. vaccae, (ix) the M.Jlavescens cluster, and (x) M. chelonae subsp. abscessus. Our phylogenctic analysis confirmed the validity of the phenotypically defined species mentioned above, but our conclusions disagree with most of the conclusions about intrageneric relationships derived from numerical phenetic analyses.-Authors' Abstract
Plikaytis, B. B., Plikaytis, B. D., Yakrus, M. A., Butler, W. R., VVoodley, C. L., Silcox, V. A. and Shinnick, T. M. Differentiation of slowly growing mycobacterium species, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, by gene amplification and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30(1992)1815-1822.
A two-step assay combining a gene amplification step and a restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis was developed to differentiate the Mycobacterium species that account for > 90% of potentially pathogenic isolates and > 86% of all isolates in clinical laboratories in the United States. These species are M. tuberculosis, M. bovis, M. avium, M. intracellulare, M. kansasii, and M. gordonae. With lysates of pure cultures as the template, two oligonucleotide primers that amplified an approximately 1,380-bp portion of the hsp65 gene from all 139 strains of 19 Mycobacterium species tested, but not from the 19 non-Mycobacterium species tested, were identified. Digestion of the amplicons from 126 strains of the six most commonly isolated Mycobacterium species with the restriction enzymes BstNI and Xhol in separate reactions generated restriction fragment patterns that were distinctive for each of these species, except for those of M. tuberculosis and M. bovis, which were not distinguishable. By including size standards in each sample, the restriction fragment profiles could be normalized to a fixed distance and the similarities of patterns could be calculated by using a computer-aided comparison program. The availability of this data base should enable the identification of an unknown Mycobacterium strain to the species level by a comparison of the restriction fragment pattern of the unknown with the data base of known patterns.-Authors' Abstract
Pretet, S., Lebeaut, A., Parrot, R., Truffot, C, Grosset, J. and Dinhxuan, A. T. Combined chemotherapy including rifabutin for rifampicin and isoniazid resistant pulmonary tuberculosis. Eur. Respir. J. 5(1992)680-684.
A prospective multicenter open study has been conducted in France in order to assess the efficacy and tolerability of an antimycobacterial regimen including rifabutin in the treatment of patients with pulmonary tuberculosis due to rifampin and isoniazid resistant bacilli. Patients were treated with daily rifabutin (450-600 mg), associated with companion drugs to which the organisms remained susceptible; in most cases the regimen included a fluoroquinolone. The duration of treatment was initially scheduled for a minimum period of 12 months after sputum culture conversion. Thirty-nine patients were enrolled, 23 of whom were treated for at least 12 months. Culture conversion was obtained at the end of the twelfth month in 14 out of 23 patients. Twenty-one out of 39 patients experienced adverse events. These were, however, serious enough to discontinue treatment in only four patients. These results suggest that an antimycobacterial combination including rifabutin might contribute to the treatment of multiresistant pulmonary tuberculosis.- Authors' Abstract
Rodrigo, G., Kallenius, G., Hoffman, E. and Svenson, S. B. Diagnosis of mycobacterial infections by PCR and restriction enzyme digestion. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 15(1992)41-44.
A method for the diagnosis of mycobacterial infections by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification followed by selective restriction-enzyme digestion of the PCR product was developed. The amplified DNA sequence used in this study occurs within the gene encoding for the mycobacterial 65kDa heat-shock protein which is found in all mycobacteria. However, there are minute differences in the amplified sequence from the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex compared with the corresponding sequence from the M. avium complex. These differences made it possible to rapidly identify to which mycobacterial complex a particular sample belonged by restriction-enzyme digestion of the PCR product. A total of 66 samples were tested, and all of them were correctly identified. This and similar methods should provide a sensitive, specific and rapid (within 12 hr) way of diagnosing mycobacterial infections to the species level.-Authors' Abstract
Sanderson, J. D., Moss, M. T., Tizard, M. L. V. and Hermon Taylor, J. Mycobacterium paratuberculosis DNA in Crohn's disease tissue. Gut 33(1992)890-896.
Crohn's disease has long been suspected of having a mycobacterial cause. Mycobacterium paratuberculosis is a known cause of chronic enteritis in animals, including primates, but may be very difficult to detect by culture. IS900 is a multicopy genomic DNA insertion clement highly specific for M. paratuberculosis. A polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based on the 5' region of IS900 and capable of the specific detection of a single M. paratuberculosis genome was developed. This was applied to DNA extracts of full-thickness samples of intestine removed at surgery from 40 patients with Crohn's disease, 23 patients with ulcerative colitis, and 40 control patients without inflammatory bowel disease. Stringent precautions were taken that excluded contamination artefact. M. paratuberculosis was identified in 26 of40 (65%) Crohn's disease, in 1 of 23 (4.3%) ulcerative colitis, and in 5 of 40 (12.5%) control tissues. Positive samples from Crohn's disease were from both the small intestine and colon; those from control tissues were from the colon only. All PCR internal control reactions were negative. The presence of M. paratuberculosis in a small proportion of apparently normal colonic samples is consistent with a previously unsuspected alimentary prevalence in humans. The presence in two thirds of Crohn's disease tissues but in less than 5% of ulcerative colitis tissues is consistent with an etiological role for M. paratuberculosis in Crohn's disease.-Authors' Abstract
Seydel, J. K., Schaper, K. J. and Rusch Gerdes, S. Development of effective drug combinations for the inhibition of multiply resistant mycobacteria, especially of the Mycobacterium avium complex. Chemotherapy 38(1992)159-168.
Rationally designed combinations of rifampin (RAMP) and thiacetazone plus isonicotinic acid hydrazide and/or ethambutol are highly effective in the treatment of patients (including HIV-positive) infected with multiply resistant mycobacteria of the Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC). Clinical results are very promising. The high efficacy of these combinations is due to the synergistic potentiation of single-drug activities. As soon as rifabutin is marketed, it should replace RAMP in the combination treatment of patients with highly RAMPresistant MAC bacteria. -Authors' Abstract
Stead, W. W. Genetics and resistance to tuberculosis -could resistance be enhanced by genetic engineering. Ann. Intern. Med. 116(1992)937-941.
Recent observations strongly suggest a significant role for genetic factors in innate resistance to infection by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. This relation was discovered in a study of tuberculosis in Arkansas, U.S.A., nursing homes and was supported by data from three outbreaks of tuberculosis in two prisons. A person's resistance level was found to correlate with the region of his or her ancestry. Ancestors of persons in the more-resistant group tended to derive from densely populated areas and cities rife with tuberculosis; whereas the ancestors of persons in the more-susceptible group tended to derive from areas once free of tuberculosis. In accordance with current genetic theory, those persons who are less resistant to tuberculosis would be expected to be more resistant to infections endemic to the region once inhabited by their ancestors. Isolation of the gene previously shown to confer specific innate (nonimmune) resistance to tuberculosis should result in the creation of a more rational approach to increasing the capacity of human macrophages to kill tubercle bacilli without producing a positive tuberculin skin test.-Author's Abstract
Vercellone, A., Riviere, M., Fournie, J. J. and Puzo, G. Specific binding of phenolic glycolipid antigens from Mycobacterium bovis BCG with antibodies. FEBS Lett. 303(1992)22-26.
We studied the molecular binding specificity of two rabbit polyclonal sera generated against phenolic glycolipid antigens, namely, PheGl B and PheGl B-3 from Mycobacterium bovis BCG. PheG 1 B is the wellknown mycoside B (2-O-Me-alpha-L-Rhap 1 → aglycone), while PheG 1 B-3 is a recently found glycolipid (alpha-L-Rhap-(l → 3)-2-O-Me-alpha-L-Rhap 1 → aglycone). The interaction specificity was mainly explained in terms of the cavity volume of the antibodies paratope. The anti-PheGl B antibodies paratope fits the 2-O-Me-alpha-L-Rhap ligand, while that of anti-PheGl B-3 binds the disaccharide moiety of PheG 1 B-3, and, with a higher affinity, the monosaccharidic unit localized at the nonreducing end. The B-3 antigen affinity is higher than that of antigen 13 for their homologous antibodies. This can be explained by the fact that the antibodies against phenolic glycolipid B-3 bind optimally to two sequential glycosyl residues suggesting the presence of two subsites. The immunoglobulin subsite with the major affinity binds the monosaccharide unit localized at the nonreducing end. -Authors' Abstract
Vijayan, V. K., Reetha, A. M., Jawahar, M. S., Sankaran, K. and Prabhakar, R. Pulmonary eosinophilia in pulmonary tuberculosis. Chest 101(1992)1708-1709.
Three radiologically and bacteriologically confirmed pulmonary tuberculosis patients had eosinophilic pneumonia, as demonstrated by broncho-alveolar lavage. In two patients, pulmonary eosinophilia was present only at the site of the lesion and the third had eosinophilia in both peripheral blood and lung. There was complete elimination of the eosinophilic inflammatory process in two patients who had successfully completed antituberculosis treatment.- Authors' Abstract
Vordermeier, H. M., Harris, D. P., Mehrotra, P. K., Roman, E., Elsaghier, A., Moreno, C. and Ivanyi, J. M. tuberculosis-complex specific T-cell stimulation and DTH reactions induced with a peptide from the 38-kDa protein. Scand. J. Immunol. 35(1992)711-718.
An immunodominant T-cell-stimulatory epitope located near the carboxy terminus of the 38-kDa antigen from M. tuberculosis (38.G, residues 350-369) was found to be M. tuberculosis-complex specific. This was demonstrated by the presence of proliferative and delayed-type hypersensitivity (DTH) responses in mice immunized with M. tuberculosis and M. bovis BCG; whereas mice immunized with M. avium or other nontuberculous species of mycobacteria showed no such responses. Peptide 38.G stimulated the proliferation of peripheral blood lymphocytes from healthy purified protein derivative (PPD)-positive individuals, but not from PPD-negative individuals. It also elicited DTH responses in M. tuberculosis-sensitized mice and in PPDpositive healthy human volunteers. Peptide 38.G could therefore prove to be an important component in any new molecularly defined reagent used in the immunodiagnosis of tuberculous infection. -Authors' Abstract
Wallace, R. J., Brown, B. A. and Onyi, G. O. Skin, soft tissue, and bone infections due to Mycobacterium chelonae chelonac- importance of prior corticosteroid therapy, frequency of disseminated infections, and resistance to oral antimicrobials other than clarithromycin. J. Infect. Dis. 166(1992)405-412.
Little is known of clinical disease due to Mycobacterium chelonae chelonae. Onehundred skin, soft tissue, or bone isolates of this rapidly growing mycobacterium were identified over 10 years. Clinical disease included disseminated cutaneous infection (53%), localized cellulitis, abscess, or osteomyelitis (35%); and catheter infections (12%). Underlying conditions with disseminated infection included organ transplantation, rheumatoid arthritis, and autoimmune disorders; 92% involved corticosteroid use. Trauma and medical procedures were risk factors for localized infections. Corticosteroids and chronic renal failure were risk factors for catheter infections. Overall, 62% of patients were receiving corticosteroids and 72% were immunosuppressed. MICs of six oral antimicrobials were obtained for 180 isolates by broth microdilution. Up to 20% of isolates were susceptible to doxycycline, ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, and sulfamethoxazole. In contrast, 100% were susceptible to clarithromycin (MICs < 1 µg/ ml). Disease due to M. chelonae chelonae usually occurs in the setting of corticosteroid therapy and is often disseminated; the organisms require high MICs of oral antimicrobials other than clarithromycin.-Authors' Abstract
Wayne, L. G., Hollander, D., Anderson, B., Sramek, H. A., Vadheim, C. M. and Rotter, J. I. Immunoglobulin-A (IgA) and IgG serum antibodies to mycobacterial antigens in Crohn's disease patients and their relatives. J Clin. Microbiol. 30(1992)2013-2018.
Sera from patients with Crohn's disease, their relatives, their spouses, and unrelated healthy controls were assayed by enzymelinked immunosorbent assay for immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgA antibodies to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, M. avium, and M. gorclonae. The patients had significantly higher IgA responses to mycobacterial antigens than did either their relatives or the controls. On the other hand, both the patients and their relatives had significantly higher IgG responses against these antigens than did the controls. The elevated IgA response was more pronounced against isopentanol-extracted whole bacterial cells than it was against soluble protein extracts, and it appeared to be directed against fixed surface antigens that lie under the loosely bound peptidoglycolipid or glycolipid antigens of mycobacteria.-Authors' Abstract
Wolinsky, E. Mycobacterial diseases other than tuberculosis. Clin. Infect. Dis. 15(1992)1-12.
The incidence of tuberculosis in the United States declined steadily until 1985, while at the same time, for at least the past 15 years, the frequency of disease attributable to other mycobacteria increased both in actual numbers and in the proportion of the total burden of mycobacterioses. Chronic pulmonary disease, lymphadenitis in children, skin and soft-tissue involvement, and infections of the skeletal system were predominant, and the principal etiologic agents were Mycobacterium avium/M. intracellulare complex, M. kansasii, M. marinum, M. fortuitum/M. chelonae complex, and M. scrofulaceum. Since 1986 disseminated disease has become not only more common, especially in association with opportunistic infections in patients with AIDS, but also attributable in part to the growing population of patients who are immunocompromized because of malignancy, receipt of an organ transplant, and administration of steroids. Treatment of these patients has been difficult because of the frequency of severe underlying conditions and the natural resistance of most of the nontuberculous mycobacteria to the presently available drugs.-Author's Abstract
Wood, P. R., Corner, L. A., Rothel, J. S., Ripper, J. L., Fifis, T., McCormick, B. S., Francis, B., Melville, L„ Small, K., DeWitte, K., Tolson, J., Ryan, T. J., Delisle, G. W., Cov, J. C. and Jones, S. L. A field evaluation of serological and cellular diagnostic tests for bovine tuberculosis. Vet. Microbiol. 31(1992)71-79.
This paper describes the field evaluation of a serological test and a new in vitro assay for cell-mediated reactivity for the diagnosis of bovine tuberculosis. The use of a Mycobacterium bovis-specific antigen (MPB70) in an ELISA to test the serological response to tuberculosis infection resulted in a specificity of 96.4% and a sensitivity of 18.1%. The most favorable results were obtained with the interferon gamma (IFNgamma) assay which had a sensitivity of 81.8% and a specificity of 99.1%. Respective figures for the single intradermal tuberculin test were 68.1% and 96.7%. The use of MPB-70 as the antigen in the IFNgamma assay reduced the sensitivity of this assay, without producing any useful increase in specificity. The IFN-gamma assay was also demonstrated to be a practical diagnostic test for use with large groups of cattle.-Authors' Abstract
Yajko, D. M., Nassos, P. S., Sanders, C. A., Gonzalez, P. C. and Hadley, W. K. Comparison of the intracellular activities of clarithromycin and erythromycin against Mycobacterium avium complex strains in J774 cells and in alveolar macrophages from human immunodeficiency virus type 1-infected individuals. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 36(1992)1163-1165.
The intracellular activities of clarithromycin and erythromycin, alone and in combination with other antimicrobial agents, were tested against Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) strains inside mouse J774 cells and inside alveolar macrophages obtained from human immunodeficiency type 1-infected individuals. Clarithromycin alone had greater intracellular activity than erythromycin alone, and drug combinations that included clarithromycin were usually more active than combinations that included erythromycin. -Authors' Abstract
Yu, N., Kurunov, V. I., Kaledin, N. A. and Popova, A. G. [Panteleeva-effectiveness of a liposomal form of rifampicin in the treatment of experimental mouse tuberculosis.] Probl. Tuberk. 1-2(1992)13-15. (in Russian)
The therapeutic effectiveness of rifampin as a free form and a component of multilampellar phosphatidylcholine cholesterol liposomes was studied on a model of generalized tuberculosis in BALB/c mice. Rifampin as a liposomal form was found to have no advantages over its free form. Possible mechanisms of the phenomenon and prospects for using liposomes in the chemotherapy of tuberculosis are discussed.- Authors' English Abstract
Zhang, Y., Heyrn, B., Allen, B., Young, D. and Cole, S. The catalase peroxidase gene and isoniazid resistance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nature 358(1992)591-593.
Tuberculosis is responsible for 1 in 4 of all avoidable adult deaths in developing countries. Increased frequency and accelerated fatality of the disease among individuals infected with human immunodeficiency virus has raised worldwide concern that control programs may be inadequate, and the emergence of multidrug-resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis has resulted in several recent fatal outbreaks in the United States. Isonicotinic acid hydrazide (isoniazid, INH) forms the core of antituberculosis regimens; however, clinical isolates that are resistant to INH show reduced catalase activity and a relative lack of virulence in guinea-pigs. Here we use mycobacterial genetics to study the molecular basis of INH resistance. A single M. tuberculosis gene, katG, encoding both catalase and peroxidase, restored sensitivity to INH in a resistant mutant of M. smegmatis, and conferred INH susceptibility in some strains of Escherichia coli. Deletion of katG from the chromosome was associated with INH resistance in two patient isolates of M. tuberculosis. - Authors' Abstract
Zhang, Y. S., Mazurek, G. H., Cave, M. D., Eisenach, K. D., Pang, Y. J., Murphy, D. T. and Wallace, R. J. DNA polymorphisms in strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis analyzed by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis -a tool for epidemiologv. J. Clin. Microbiol. 30(1992)1551-1556.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates were studied by comparing large restriction fragment (LRF) patterns produced by digestion of chromosomal DNA with infrequent-cutting endonucleases and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Four cultures of H37Rv and 36 clinical isolates or M. tuberculosis were compared by using Dral, Asnl, Xbal, and Spel. Dral and Asnl allowed easy visual separation of 18 of 21 epidemiological unrelated strains. Xbal and Spel allowed discrimination of all 21 unrelated strains, including the 3 strains inseparable with Dral and Asnl, but comparison of LRF patterns was more tedious because of overlapping fragments. A total of 26 isolates belonging to 10 clusters of related isolates were compared by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, with all related isolates giving identical LRF patterns. These included multiple isolates from the same patient or the same family. The same grouping of clustered isolates was obtained when BamHI DNA digests were hybridized with two probes from the insertion sequence IS6110. Long-term laboratory passage of H37Rv produced minimal detectable changes in LRF patterns. LRF patterns are useful tools for epidemiologic studies of tuberculosis without the need for radioactive or specific DNA probes. -Authors' Abstract